900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
The RBI recently released the draft rules on compensation for CEOs and full-time directors of banks.
How were violations by bank executives dealt?
What are the recent developments?
What are the draft rules for?
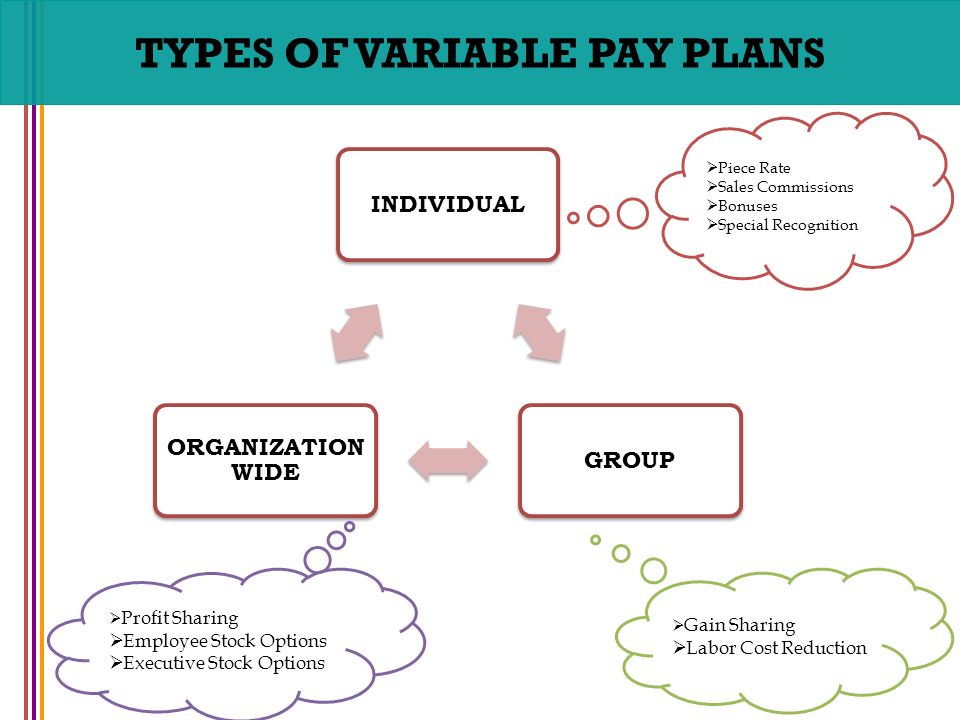
What are the key proposals in the draft?
Source: The Indian Express
Quick Fact
Financial Stability Board (FSB)