900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
The 34th ASEAN Summit was recently held in Thailand’s capital Bangkok.
Click here to read on ASEAN's RCEP decision
What is ASEAN?
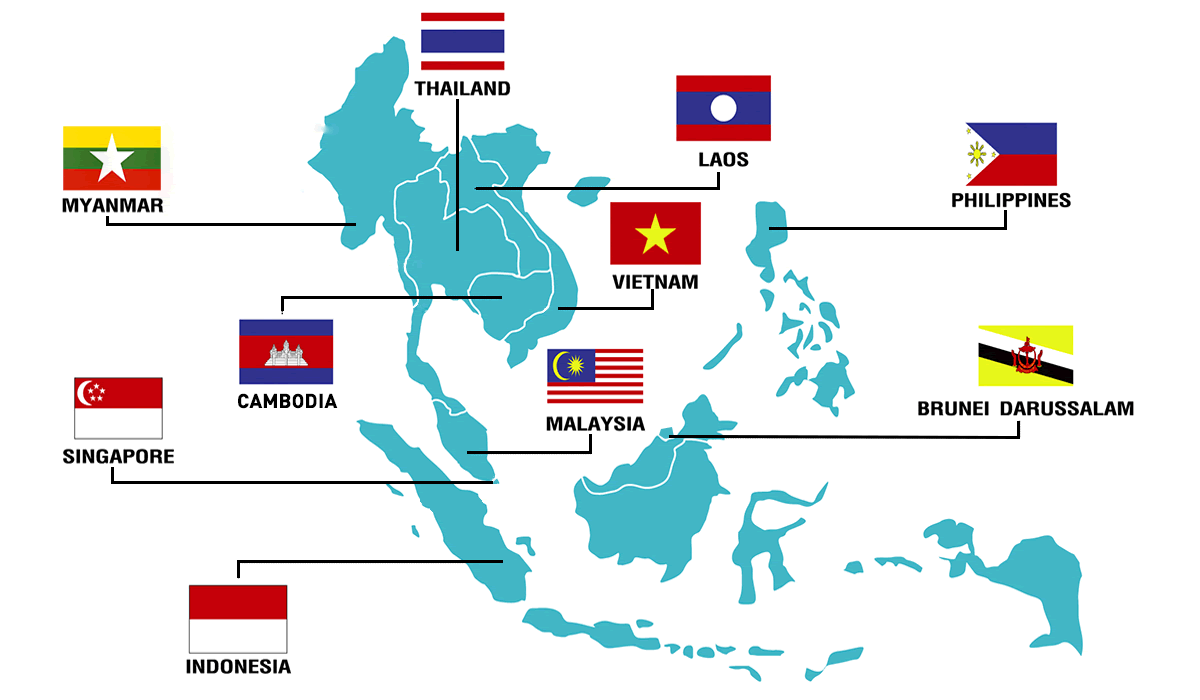
What are the key outcomes of the summit?
What is China’s stake in the region?
Source: Times of India
Related News: India-ASEAN Commemorative Summit