900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently, many incidents of smuggling freshwater turtles are reported across various States by international trafficking networks.
23rd May marks the World Turtle Day.
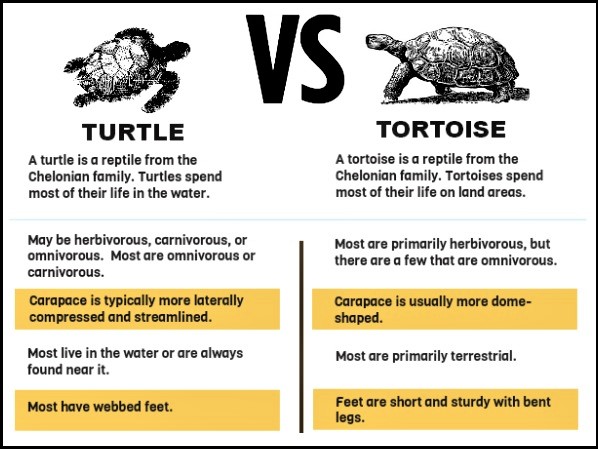
Not all turtles are tortoises, but all tortoises are technically turtles.
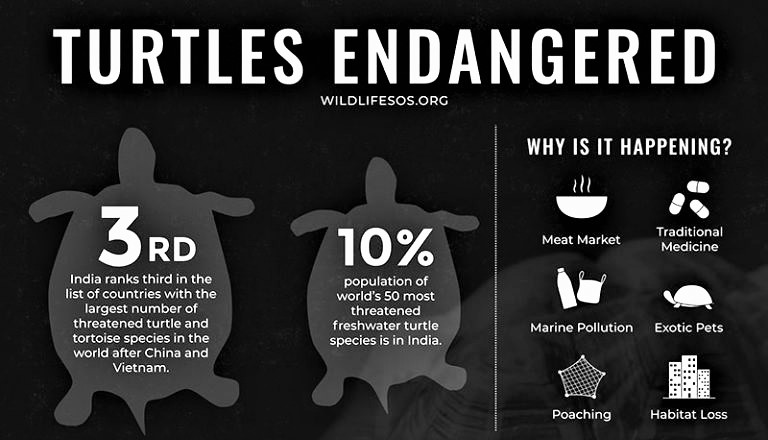
India ranks 3rd in the list of countries with the largest number of threatened turtle and tortoise species in the world after China and Vietnam.
 What efforts were taken by India for conservation of turtles?
What efforts were taken by India for conservation of turtles?
Related links - Northern River Terrapin, Indian Flapshell Turtles
Quick Facts
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
References