900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
The Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu (Merger of Union Territories) Bill, 2019 was recently introduced in the Lok Sabha.
What is the Bill on?
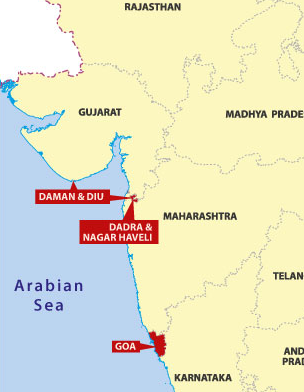
How did these territories come under Portuguese rule?
What happened after India’s independence?
What was Operation Vijay?
What happened after the Portuguese left?
Source: Indian Express