900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The lingering COVID-19 crisis is a good time to revive the universal health care (UHC).
WHO’s goal- 1 billion more people benefitting from universal health coverage by 2023.
SDG target 3.8 focuses on achieving universal health coverage.
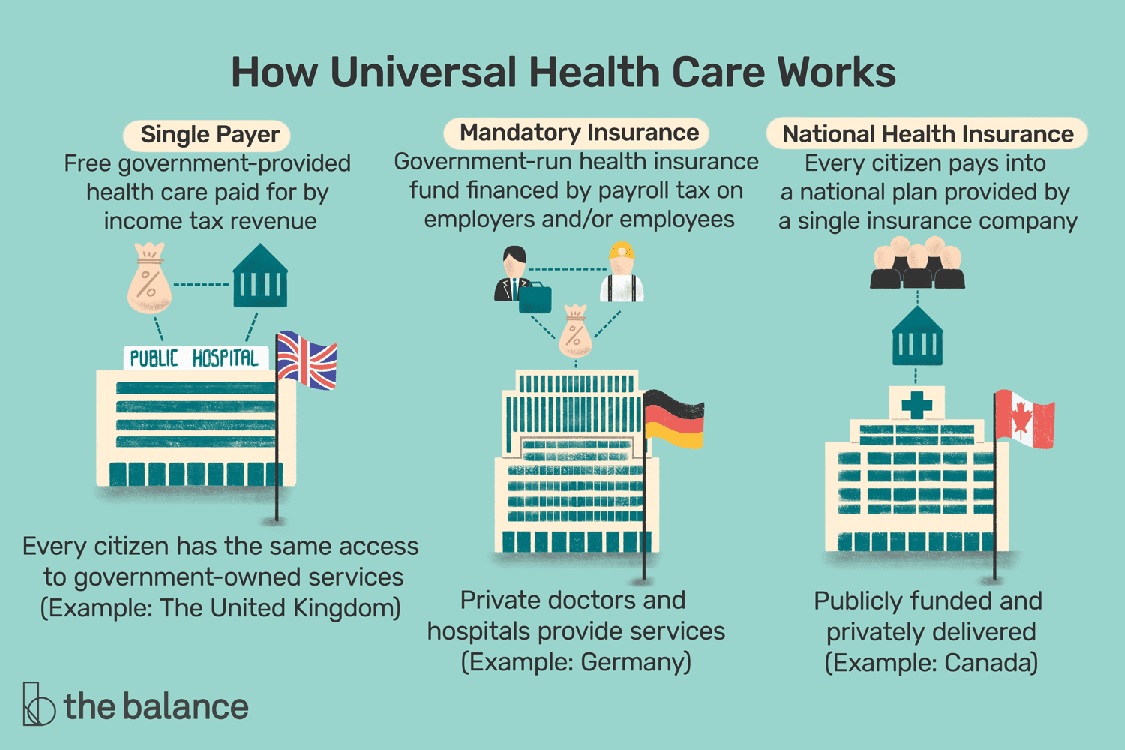
Tamil Nadu has proposed the Right to Health Bill that ensures State’s commitment to quality health care for all.
References