900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The narcotics trade is not only a social problem that harms youth and families but a national security problem as the money it generates is diverted for disruptive activities.
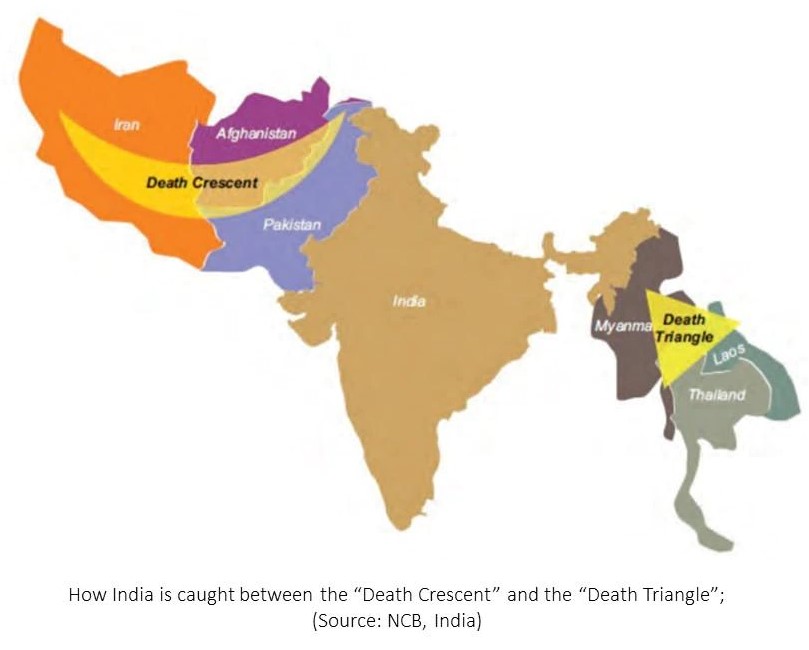
The Golden Crescent and the Golden Triangle are names given to Asia's two principal areas of illicit opium production. The Golden Crescent comprises Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan and the Golden Triangle represents the regions of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand
What can be done to prevent drug trafficking?
|
Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) |
|
.
|
Opium Cultivation in India |
|
References