900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Ladakhi innovator Sonam Wangchuk completed his 5 day climate fast in order to draw the attention of Indian leaders to the region’s fragile ecology and to secure its protection under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
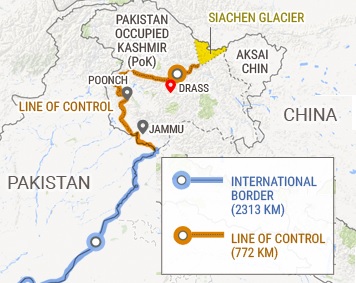
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs recommended including of Ladakh in the Sixth Schedule because its tribal communities account for 79.61% of its total population.
References