900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is G20?
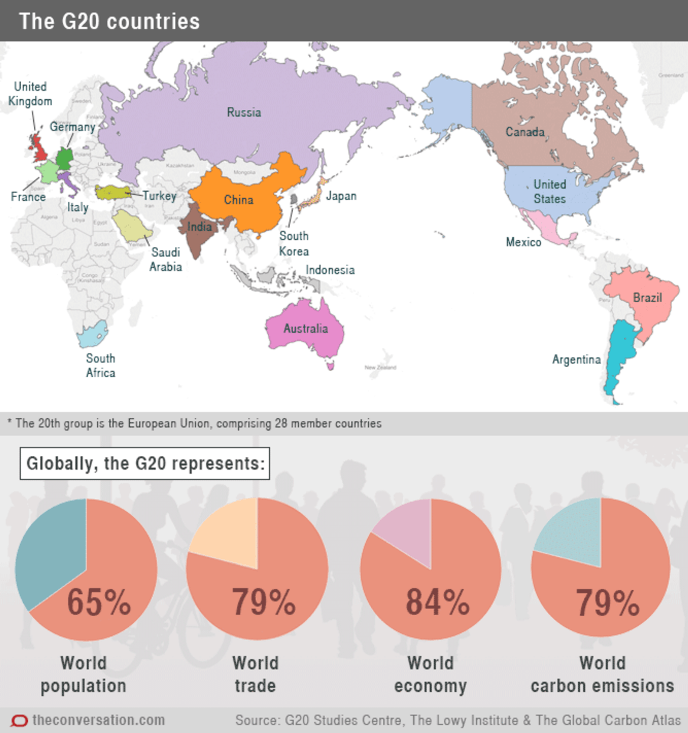
What are the general criticism against G20?
What were the outcomes of the recent G20 meet?
Why the US got sidelined?
Why India was praised at Hamburg summit?