900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
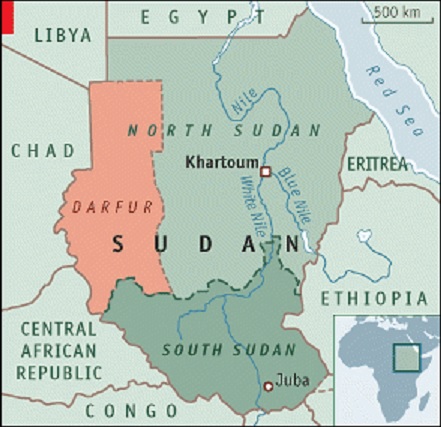
Sudan has witnessed massive protests since Abdel Fattah al-Burhan took over in a military coup and upended the country’s transition to democracy.
Reference