900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
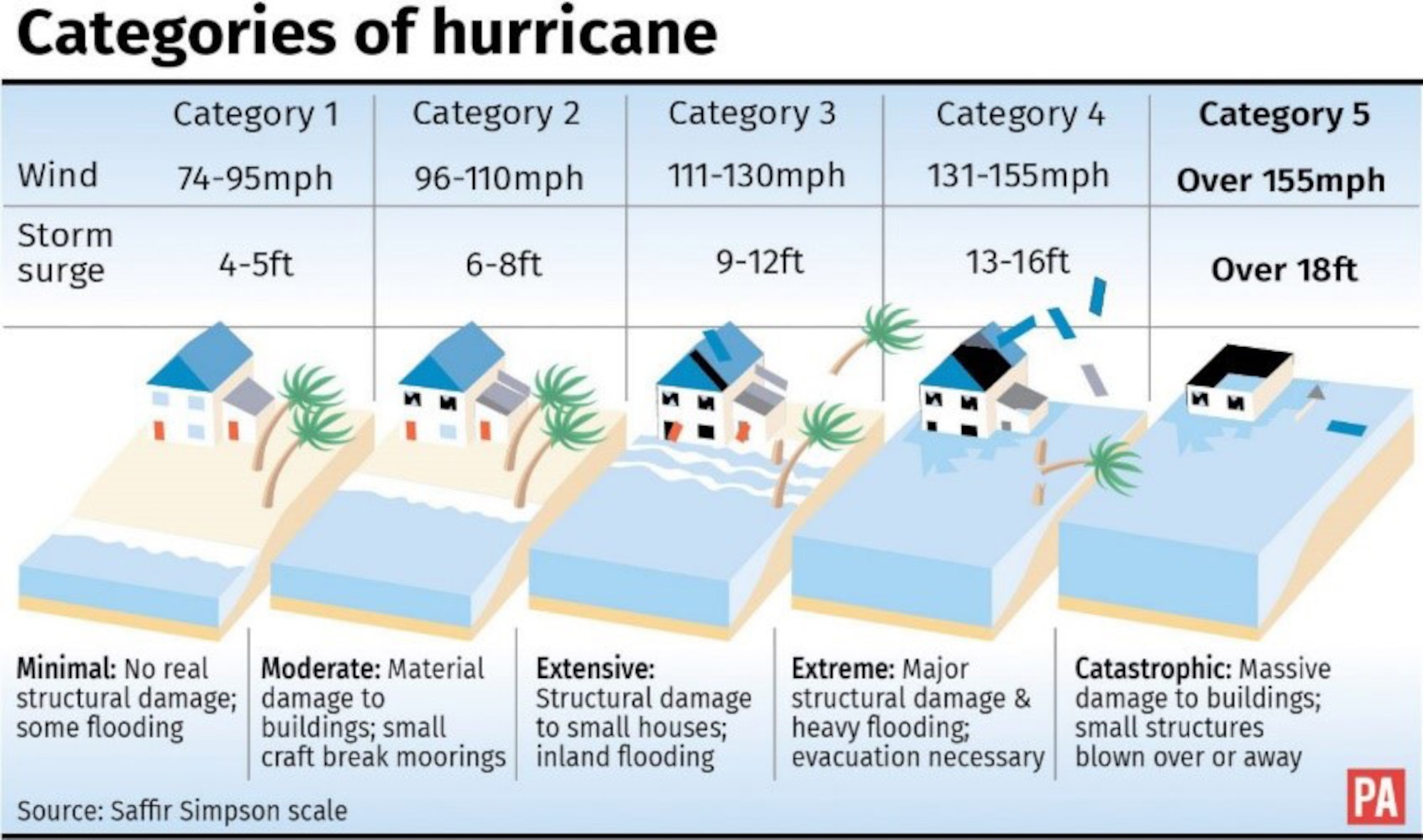
As Earth’s climate warms, more storms are undergoing rapid intensification, growing quickly from relatively weak tropical storms to Category 3 or higher hurricanes in under 24 hours.
Since 1901, sea surface temperatures have risen an average of 0.14 degrees Fahrenheit per decade.
The likelihood of a hurricane undergoing rapid intensification has increased to 5% from 1% since the 1980s.
References