900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
To achieve the export target of 2 trillion dollars by 2030, India is seriously negotiating on Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), but most FTAs happen behind closed doors with very little information available.
The Ministry of Commerce is the nodal body dealing with FTAs in India.
To know more about FTAs, click here
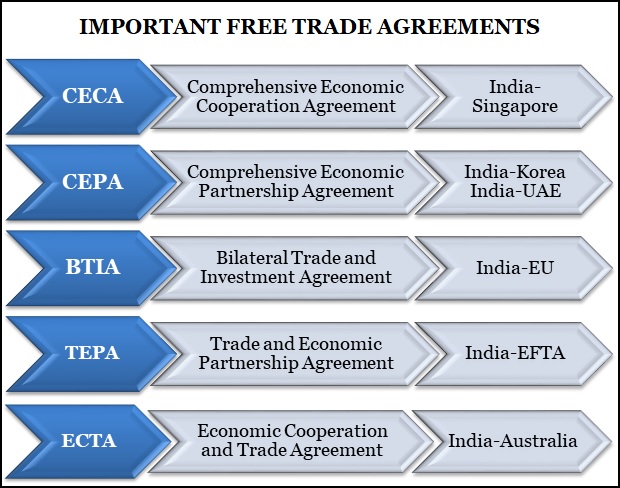
In India, entering into treaties and negotiations, signing and ratification are within the constitutional competence of Parliament.
References