900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The timing of reduction of import duty by the government has affected the balance between the interests of farmers and consumers.
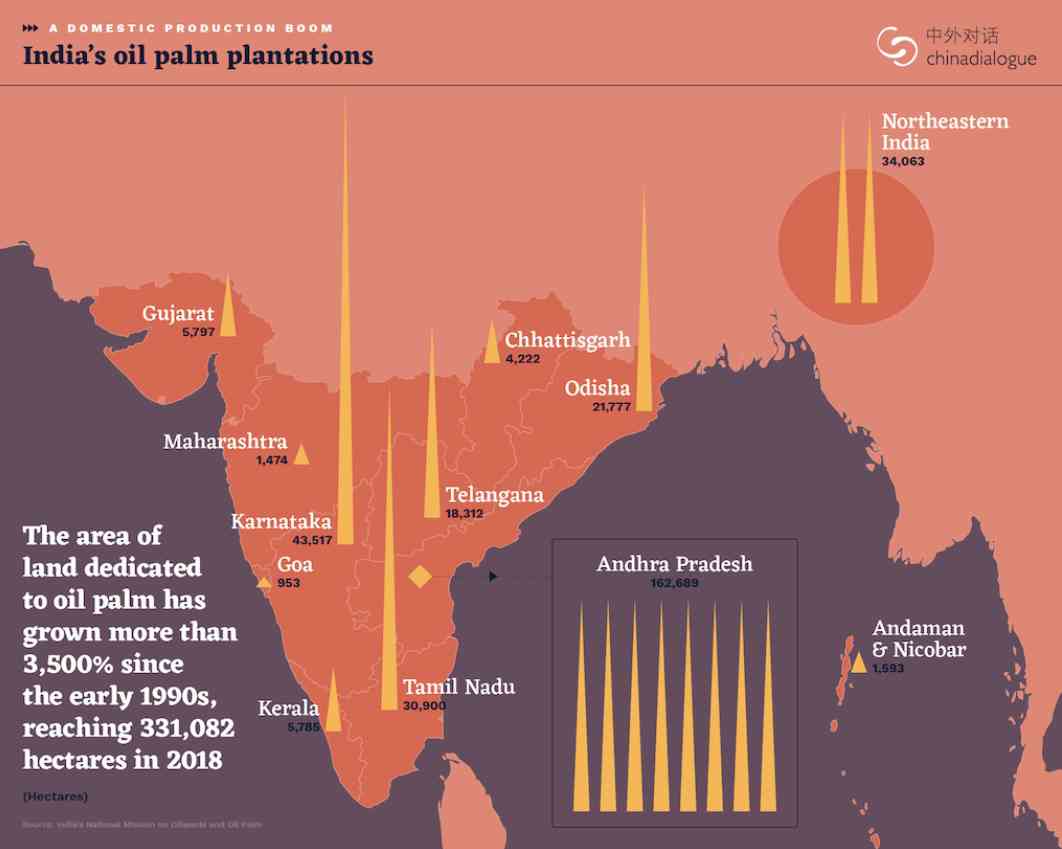
Yellow Revolution started during early 1990s aimed at self-sufficiency in oilseeds but it could not be sustained beyond a short period.
The leading exporters of palm oil worldwide were Indonesia and Malaysia.
References
1. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/editorial/frying-times/article37113088.ece