900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Children for Fishing Cat project of Andhra Pradesh recruits children as ambassadors for conservation to save the predator and its home.
The Children for Fishing Cat project is part of the Godavari Fishing Cat Project, which focuses on community-based conservation of this in the coastal habitats of the region.
|
Protection Status |
|
|
IUCN Red List |
Endangered |
|
CITES |
Appendix II |
|
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 |
Schedule I |
Reference
A recent study has identified India among the global flash drought hotspots from 1980-2015.
Reference
A report has found that the water levels of lakes in Kenya’s Great Rift Valley increased significantly, due to climate change, human activities and an active tectonic belt.
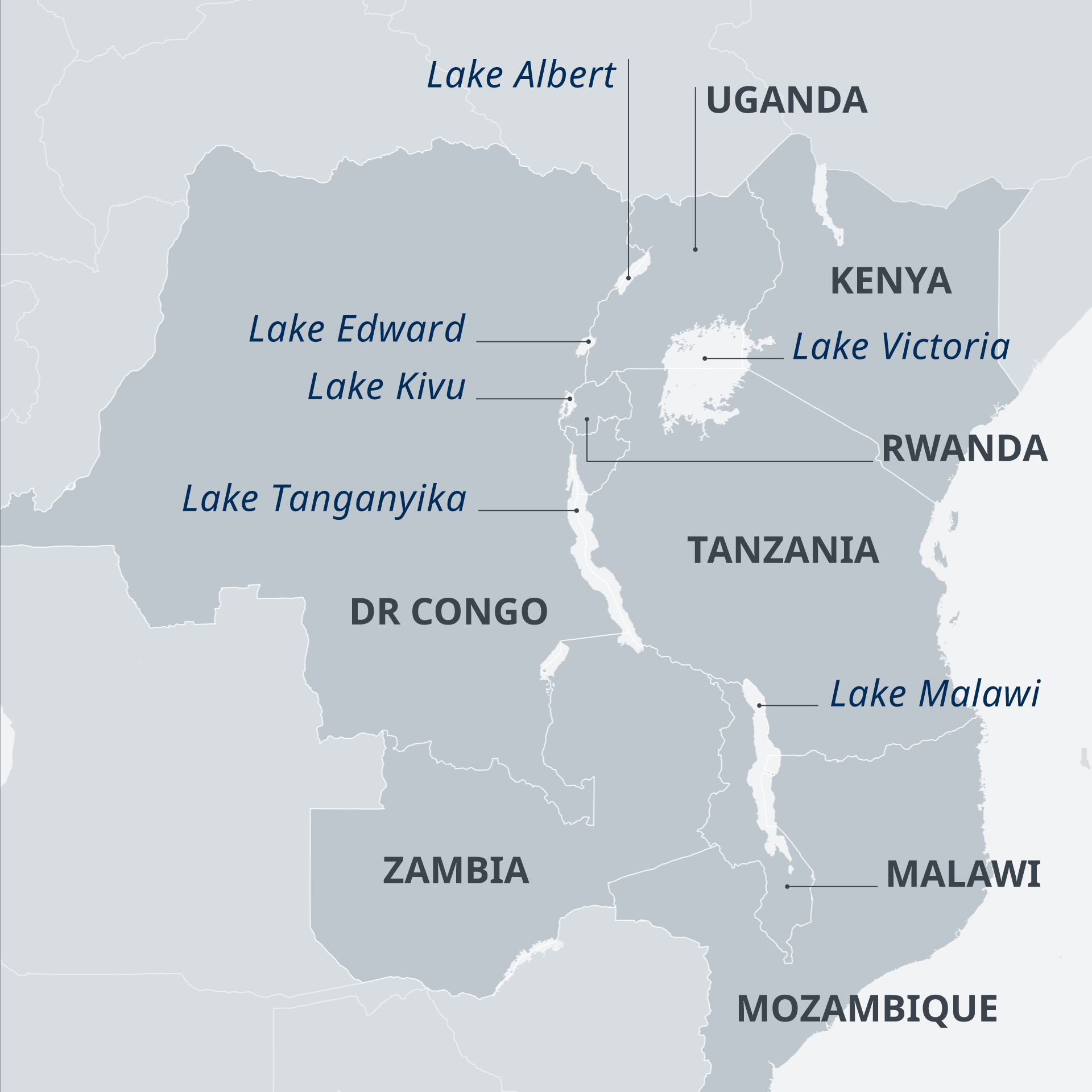
Reference