Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems-ENDS (e-cigarettes) are 95% less harmful than tobacco cigarettes claimed by a study is a myth.
References
A US pharmaceutical company has released the positive results from phase 3 trials for its drug to treat Alzheimer’s treatment, donanemab.
References
A forest department probe into the bushfires that impacted an area of about 4 sq km in Goa in March concluded that the fires were largely triggered by natural causes.
An FSI study for the period 2004-21 has found that nearly 10.66% area under forests in India is ‘extremely’ to ‘very highly’ fire-prone.
Forest Fires
References
Jyotirindra Bodhipriya Larma, an important leader of the Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHT) in Bangladesh has arrived in India.
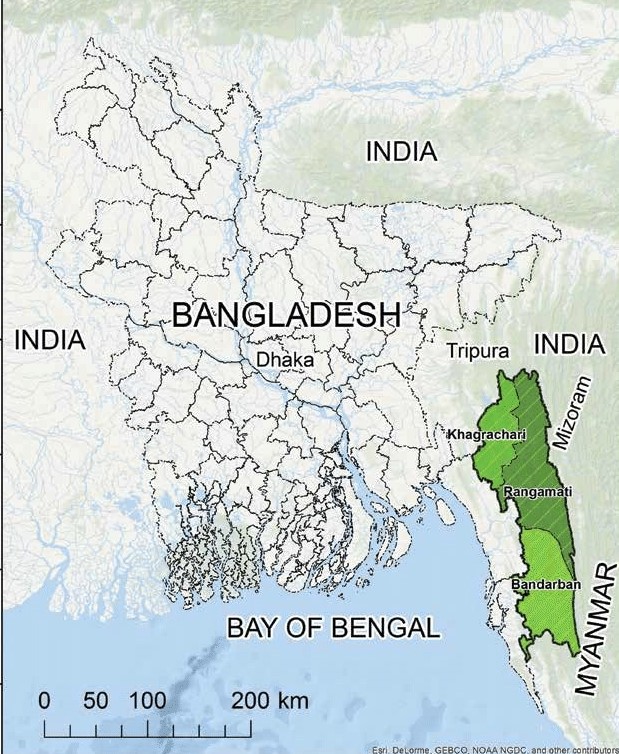
Baisabi, the festival of Chakma coincides with the Assamese festival of Bihu.
References
The Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT) is to create technical and scientific terminology in 10 Indian languages.
The national language list, when created in 1950 had 14 languages. Sindhi was added in 1967; Konkani, Manipuri, and Nepali in 1992; and Bodo, Dogri, Maithili, and Santhali in 2004.
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology
References