Reference
The Federated States of Micronesia is one of the latest places on Earth to experience an outbreak of Covid-19, after two and a half years of successfully protecting itself from the virus.
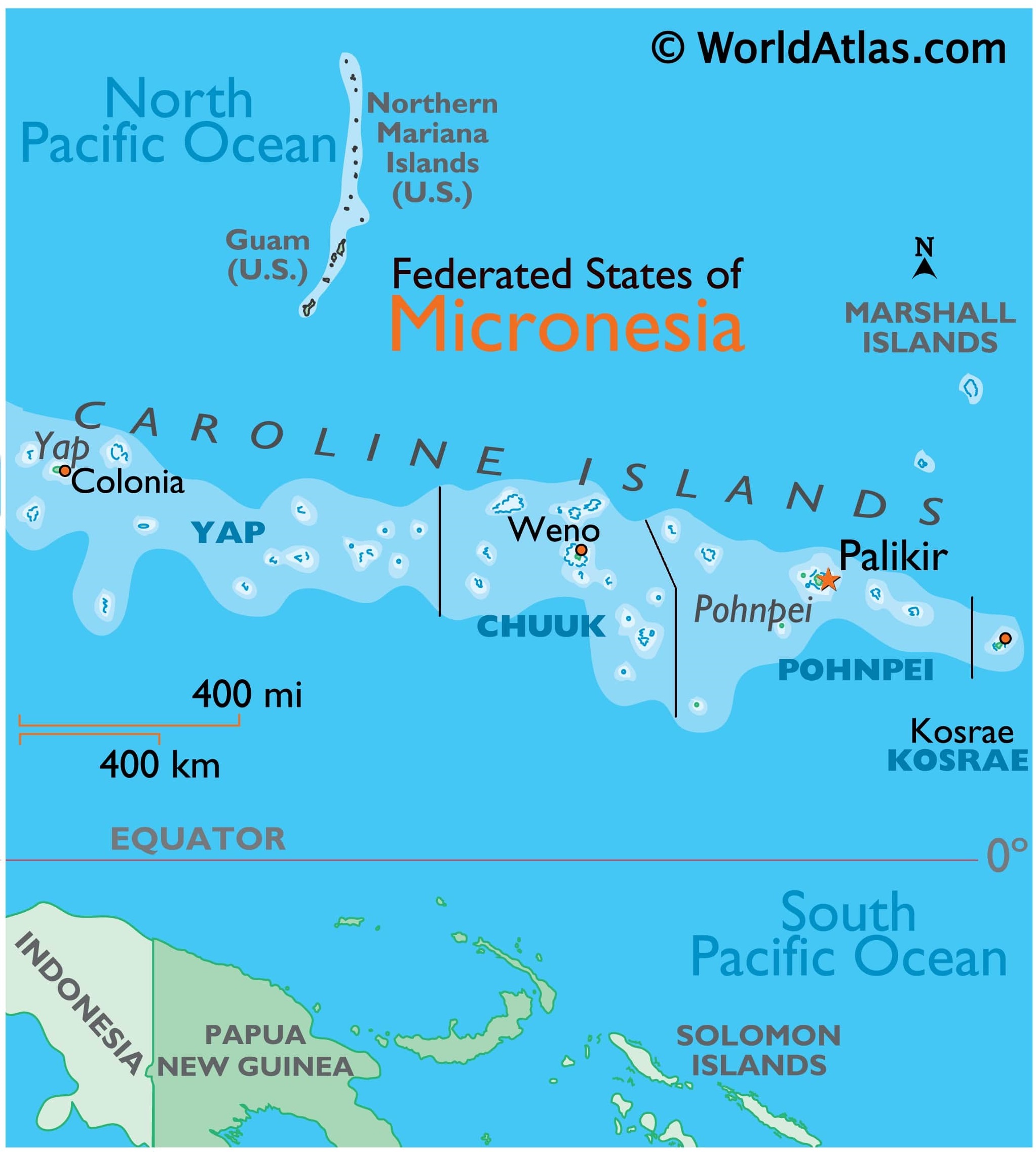
Reference
Residents of buildings on Marine Drive, the iconic 3-km promenade in south Mumbai, complained of “unusual vibrations”, during a recent high tide, that are the result of the relocating tetrapods as part of the Coastal Road Project.

Reference
The second phase of the GOAL Programme (GOAL 2.0) was launched with an aim to digitally upskill tribal youth by promoting entrepreneurship and opening up opportunities for them using digital technology.
Tribal population constitutes about 8.6% of the total population in India.
Reference
About 0.5 million people in India die every year from causes that could have been prevented by organ transplants that were not available to them.
India needs more organ donations as only 0.01% Indians have given consent to donate their organs after their death.
Reference