900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Desert Locusts
Role 0f wind in Locusts Spread in India
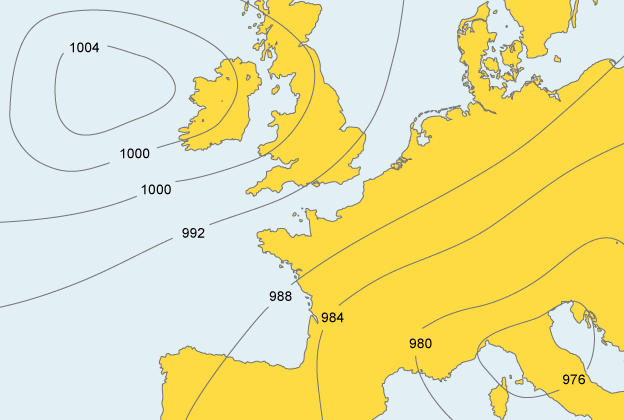
Isobars
Delimitation
Delimitation Commission
Current Position of Delimitation
Delimitation under Indian constitution
Financial Development Council
Asian Development Bank
Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat programme
UN Peace Keepers
Military Gender Advocate of the Year Award
United Nations Mission in South Sudan
Source: PIB, the Hindu, Down to Earth