900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
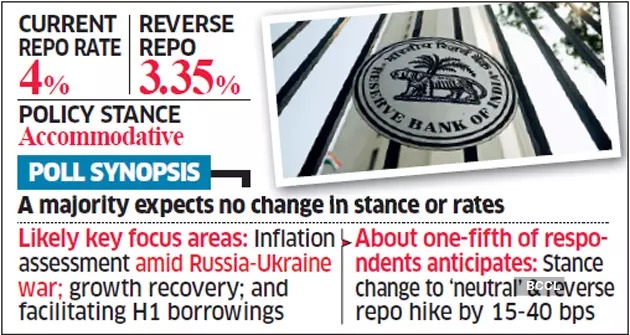
The Reserve Bank of India recently issued its monetary policy report and kept key lending rates (repo rate and reverse repo) unchanged.
Repo rate is the interest charged by the RBI when commercial banks borrow from them by selling their securities to the central bank.
Reverse repo rate is the interest rate the RBI pays to commercial banks when they store excess cash reserves with the central bank.
References