900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
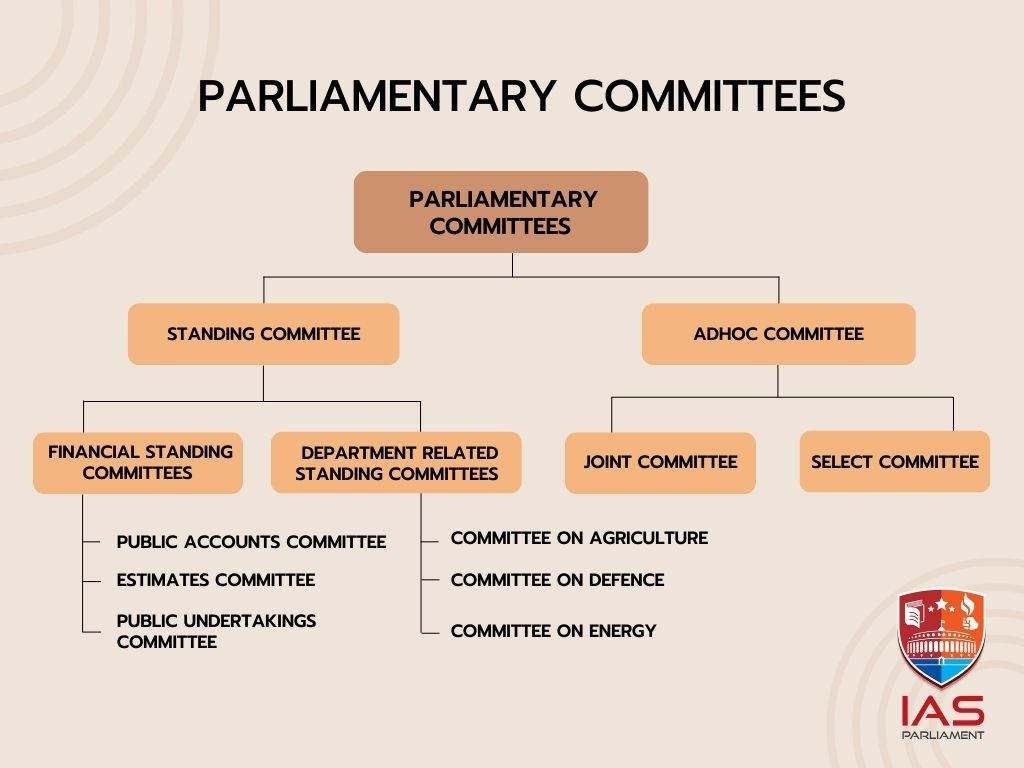
Due to continuous disruptions and adjournments in the Parliament, referring the bills to the Standing Committees may be counterproductive adding to the delay.
References
Quick facts
Departmentally Related Standing Committees (DRSCs)
Whip