900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
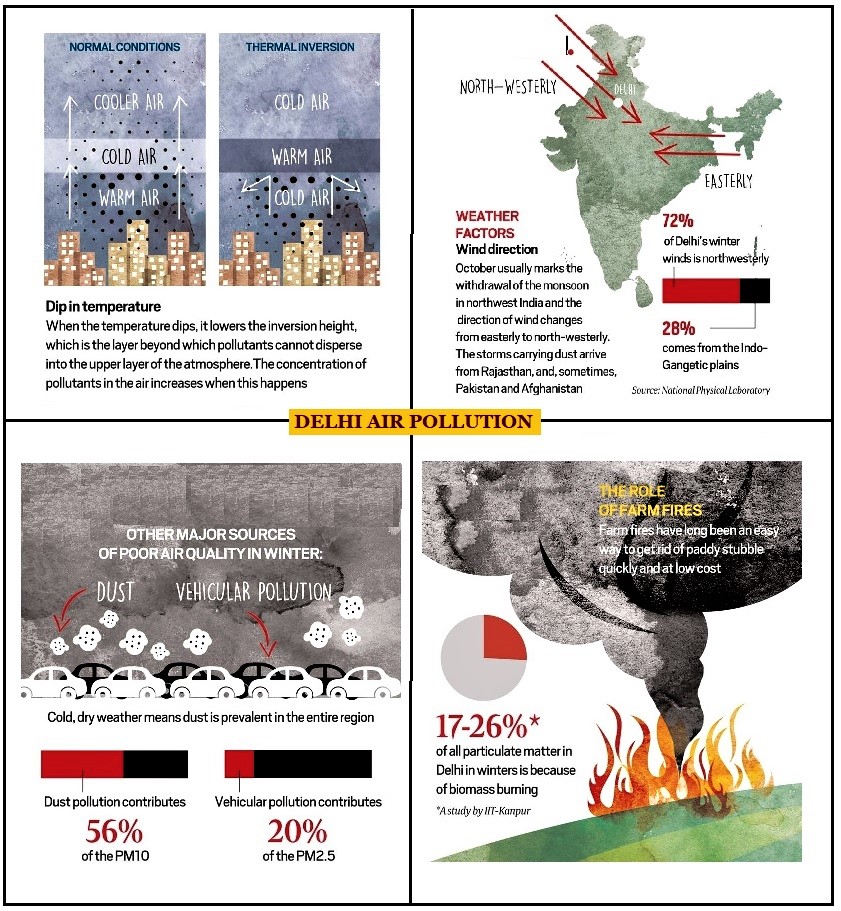
As the Air Quality Index (AQI) in Nation Capital Region dipped to the ‘severe’ category, Stage 4 of the Graded Action Plan (GRAP) has kicked in.
References
Quick facts
Graded Response Action Plan
