900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
India’s selective clampdown on rice exports has raised the eyebrows of both local traders and global commentators.
Broken or ground rice refers to the fragments of rice grain obtained by milling. Parboiled rice refers to the rice when the paddy is soaked in water, steamed and dried while retaining its outer husk.
To know about India’s export restriction on wheat, click here
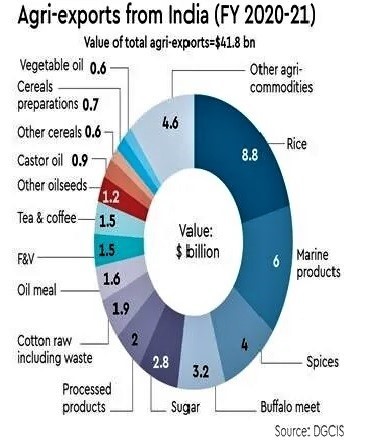
India is the world’s second-largest rice producer after China.
|
India’s total rice exports (2021-22) |
212.1o LMT |
|
Non-basmati Rice |
172.62 LMT |
|
Basmati Rice |
39.46 LMT |
References