900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
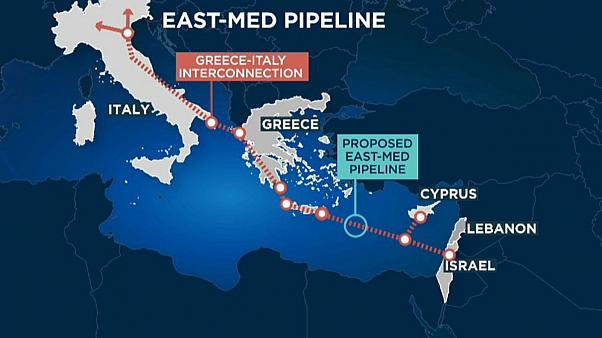
While world’s attention has been focussed on the controversy of European and US opposition to Nord Stream II pipeline from Russia to Germany, it was a European Pipeline project (EastMed) that met a quiet death.
The US has only 5% of global gas reserves but is the world's biggest gas exporter whereas Russia has 24% of proven gas reserves of the planet.
References