900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
In the post-pandemic era, China is positioning itself to cause an unprecedented change in industrialisation.
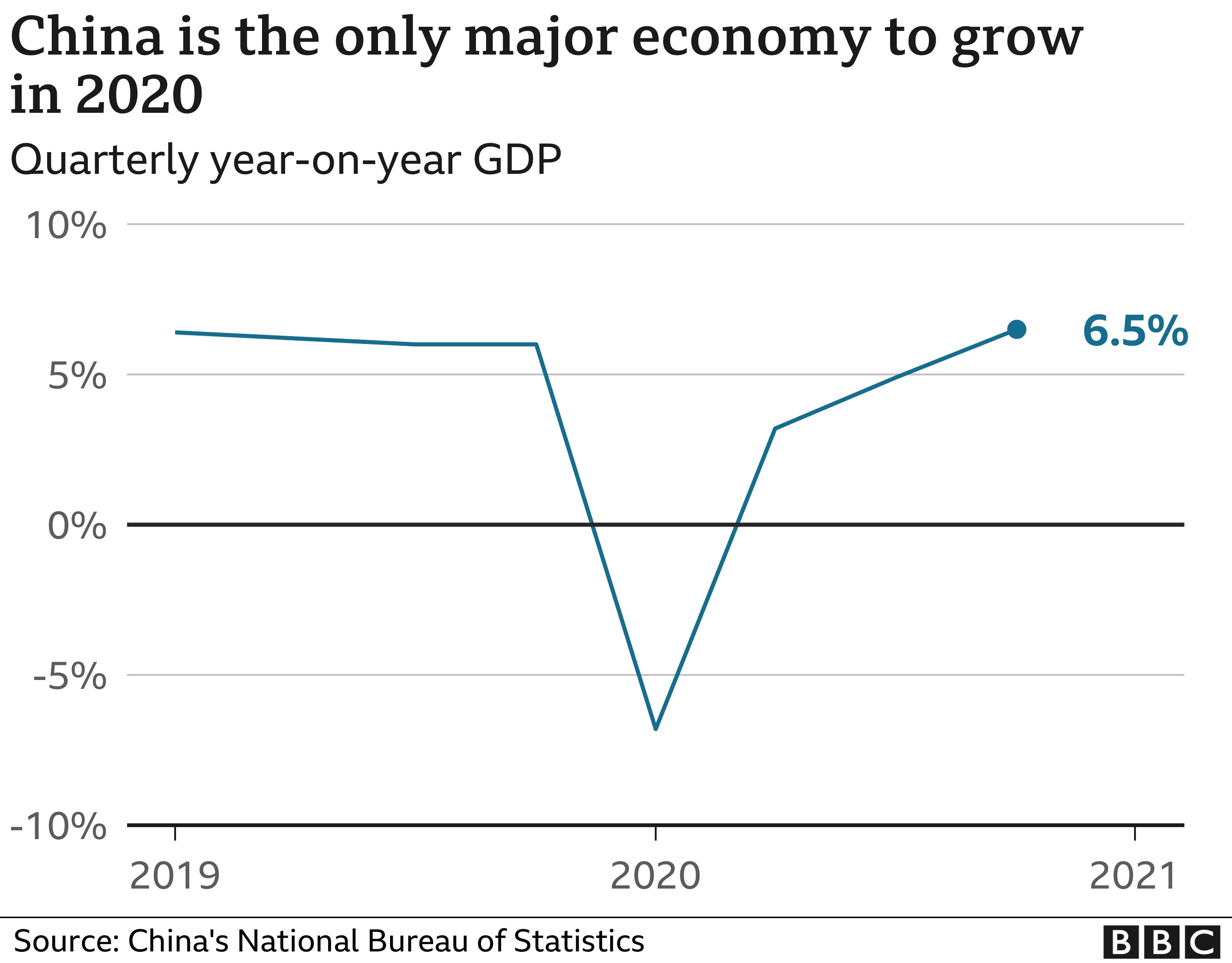
China accounts for about 30% of global manufacturing. China was the world’s biggest exporter in 2020-21, accounting for 13% of world exports and 18% of world market capitalisation.
China has overtaken the U.S. in AI patent applications and in terms of the number of AI research publications and journal citations.
References