900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
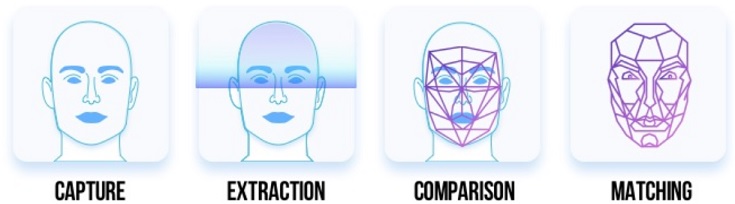
Clearview AI, an American facial recognition company has scraped images from across the Internet to design a powerful facial recognition tool, rekindling the debates on the private play in FRT.
References