900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
SC power for complete Justice
Changes in Labour Laws
International Labour Organization
Ban on TB Drugs on crops
Streptomycin
Integrated Pest Management
Central Insecticides Board & Registration Committee
Mission Sagar
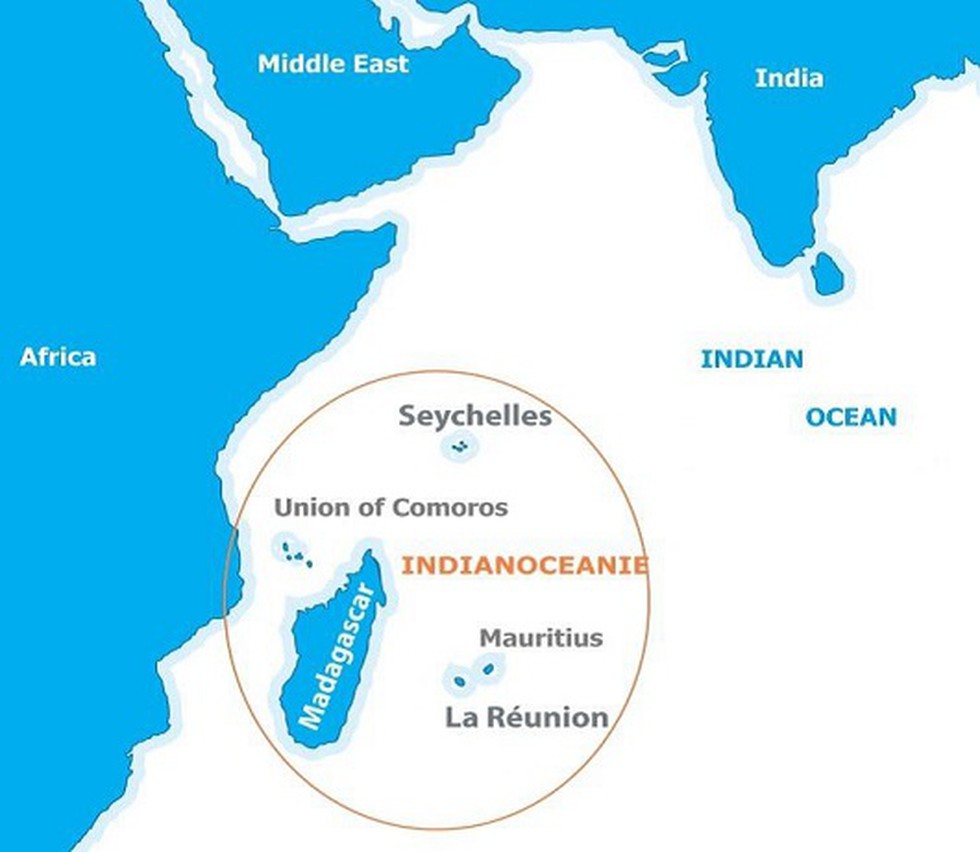
Indian Ocean Commission
SAGAR
DRUVS Cabinet

Notes Clean

NASA Perseverance Rover
Mastcam-Z
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Down to Earth