The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently celebrated its 90th year in Mumbai.
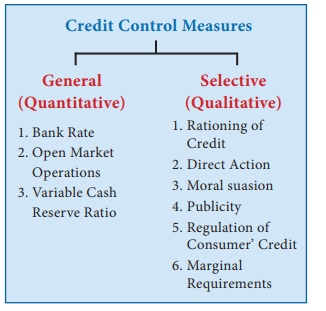
|
Major contributions of RBI |
|
|
Initiatives |
About |
|
Green Revolution Package (1960s-1970s) |
It played a pivotal role in supporting this initiative by providing credit facilities to farmers, promoting agricultural mechanisation, and implementing policies to enhance rural credit accessibility. |
|
Nationalization of banks, 1969 |
It was implemented under the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act of 1970, to better serve the needs of development of the economy in conformity with national policy objectives. |
|
Priority Sector Lending, 1972 |
It provides timely and sufficient credit to key sectors of the economy that might otherwise face difficulties in accessing funds |
|
Liberalization of Indian economy, 1991 |
It refers to the series of policy changes aimed at opening up the country's economy to the world, with the objective of making it more market-oriented and consumption-driven. |
|
TReDS, 2014 |
It is an electronic platform where MSMEs can sell their receivables at a competitive rate to financiers, including banks and non- banking financial companies (NBFCs), through an auction mechanism. |
|
Unified Payment Interface (UPI), 2016 |
It was launched by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to provide seamless and instant experience to users across India. |
|
Inflation Targeting Framework, 2016 |
Under this framework, the RBI set a target for inflation and adjusted monetary policy instruments to achieve it, the banking regulator has set an inflation target of 4%, with a tolerance band of +/- 2%. |
|
Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), 2019 |
It was launched by NPCI, which is an integrated bill payment system that offers interoperable and accessible bill payment services to customers through a network of agents or online channels. |
|
Aadhar-based eKYC, 2019 |
The Aadhaar eKYC process enables financial institutions to authenticate customers’ identities remotely, without the need for physical documentation. |
|
Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) , 2020 |
To provide immediate credit assistance to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. |
|
Account Aggregator, 2021 |
The framework allows customers to manage their financial data from various financial entities in a secure and seamless manner through a consent-based mechanism. |