900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
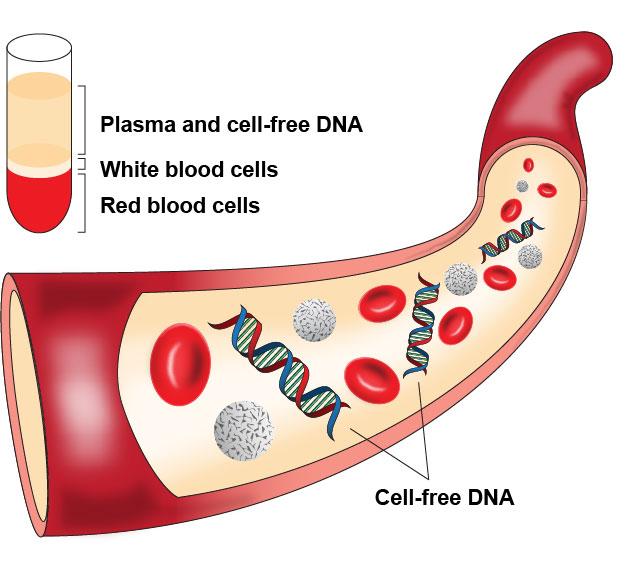
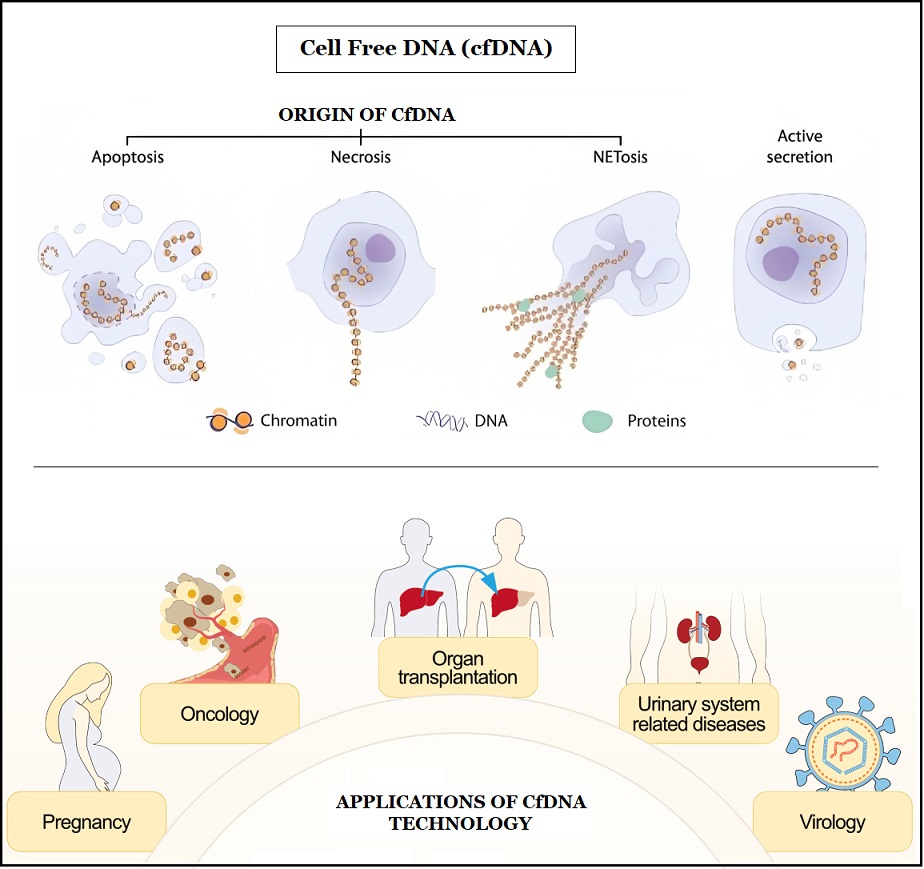
Cell free DNA is found to be promising in the field of disease discovery.
DNA is a molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism.
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)
Reference