The 14th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS) was held in the historic city of Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
|
Convention of Migratory Species (CMS) |
|
|
Key aspects |
About |
|
Conception |
It began at the 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment. |
|
Launch year |
1979 in Bonn, Germany (called as Bonn Convention) |
|
Entered into force |
1983 |
|
Secretariat |
Provided by United Nations Environment Program, based in Bonn in Germany on the banks of River Rhine. |
|
Depository |
Germany |
|
Out-post office |
Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. |
|
Aim |
|
|
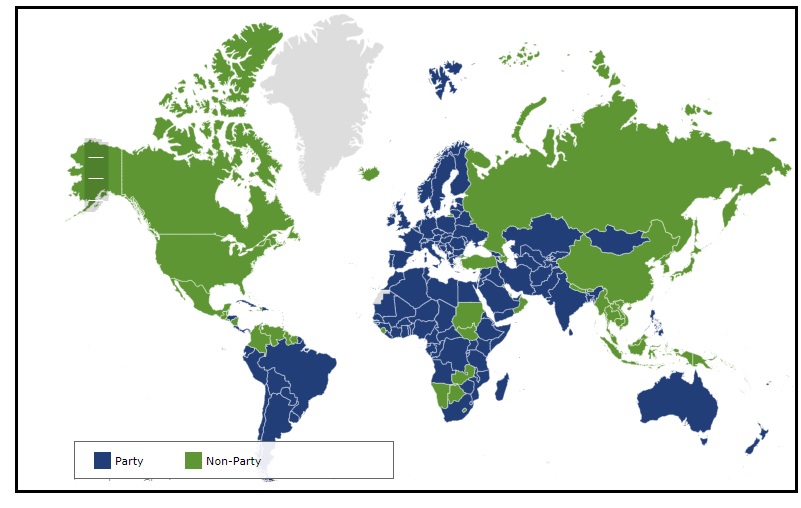
Parties |
|
|
CMS Trust Fund |
Each Party shall contribute to this budget according to a scale to be agreed upon by the COP. |
|
Listed species |
It has about 1,200 species listed in 2 Appendix
|
|
Appendix I |
It endeavour to protect them by
|
|
Appendix II |
It covers migratory species that have an unfavourable conservation status and that require international agreements for their conservation and management. |
CMS is the only global convention specializing in the conservation of migratory species, their habitats and migration routes.
CMS COP 13- The COP was held in India for the 1st time at Gandhinagar in 2020
This is the first COP of any global environmental treaty to take place in Central Asia, a region home to many migratory species including the Saiga Antelope, the Snow Leopard, and many species of migratory birds.
|
The State of the World Migratory Species |
|
New Global Partnership on Ecological Connectivity
Key findings
|
As part of CAMI, Uzbekistan announced a new programme to introduce the Cheetah in the country.
|
Ecological connectivity |
|