Earlier this month, a man and his minor son were arrested for sexually abusing a 5-year-old girl, who was related to them, for 6 months.
|
DATA POINT | SEXUAL ASSAULT IN INDIA |
|
According to the World Health Organization, Child Sexual abuse includes a child who is unable to give consent, under compulsion, fear or any other circumstances, not prepared physically, mentally or emotionally for sexual activities, any illegal activity, other activity which not relates with the moral values of the society, child trafficking, child prostitution, child pornography, and many other similar acts, which are done against the will of the child in it”.
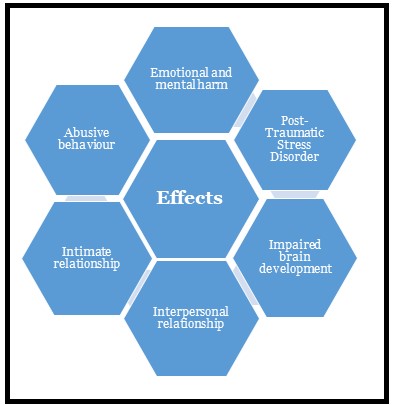
According to the United Nations (UN), a comprehensive sexuality education is a curriculum-based process of teaching and learning about the cognitive, emotional, physical and social aspects of sexuality.
Why there is a need of comprehensive sexuality education?
What are the challenges in adopting comprehensive sexuality education?
What lies ahead?
References