900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
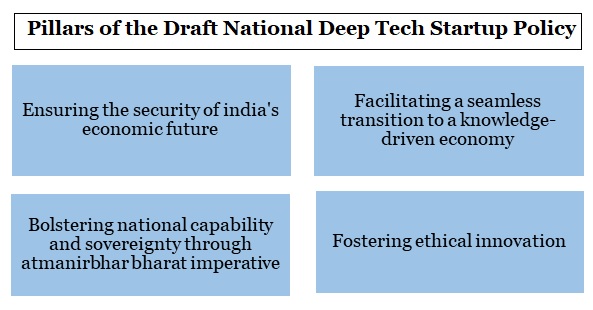
The office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government has put out a draft National Deep Tech Start-up Policy.
Deep-tech start-ups in India raised 2.7 billion dollars in venture funding in 2021, and accounts for over 12% of the country’s overall startup ecosystem, as per NASSCOM study.
|
Initiatives taken to promote deep start-ups |
|
References