900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Javier Milei, the recent winner of Argentina’s presidential election, has drawn attention for his plan to replace the country’s currency “Peso” with the dollar.
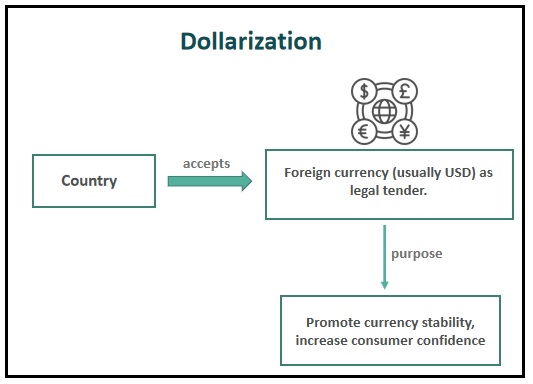
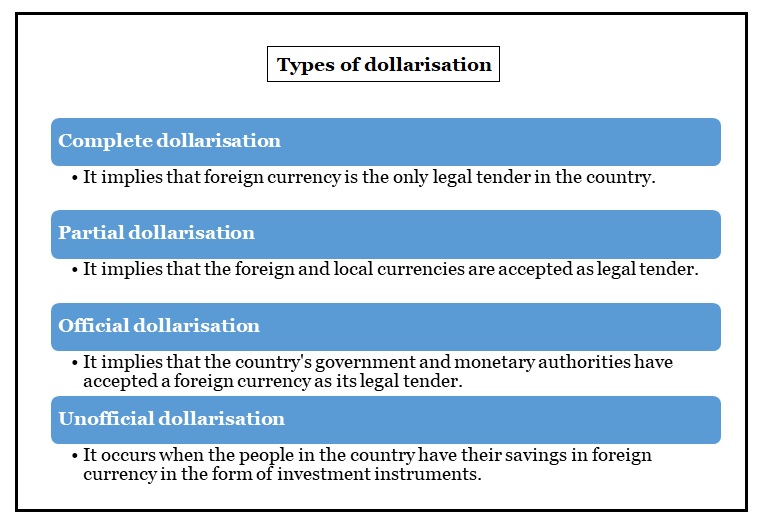
3 fully dollarised economies - Ecuador, Panama and El Salvador have had successful economic outcomes following dollarisation.
|
Ecuador model of dollarisation |
|
Seigniorage is a term that refers to the profit that a government or a central bank makes by issuing money.
|
De-dollarisation |
|
References