The importance of using mother tongue in the teaching-learning process and creating educational materials has been emphasised in the New Education Policy (NEP) and initiatives like the NIPUN Bharat Mission.
Article 29-Protection of interests of minorities- Any section of the citizens having a distinct language, script or culture of its own shall have the right to conserve the same.
To know about languages of India, click here
Neuroscientific research reveals that more than 85% of a person’s brain development takes place before the age of 6.
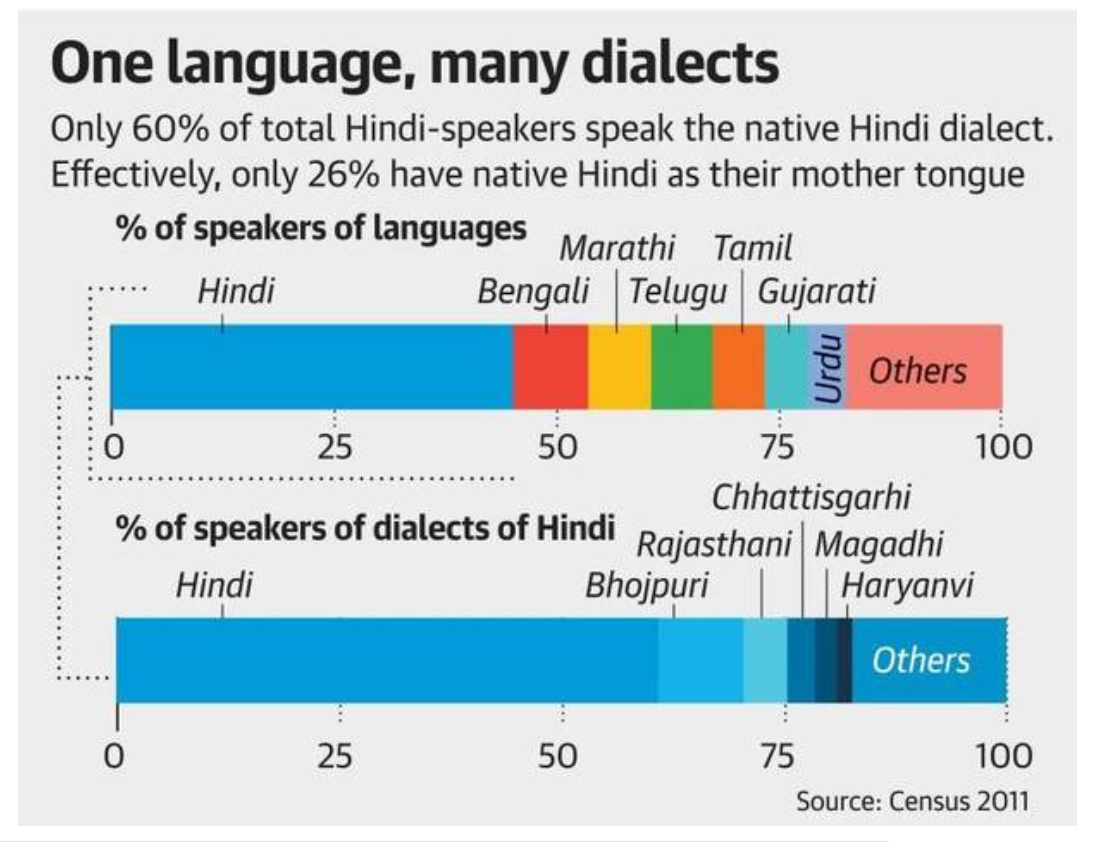
India has over 22 officially recognised languages and hundreds of dialects, each with its own unique cultural and historical significance.
|
Initiatives Taken to Promote Regional Languages |
|
References