Recently Rajya Sabha passed The Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Office and Terms of Office) Bill, 2023.
|
Constitutional Provisions for Election Commission |
|
|
About |
Description |
|
Election Commission |
It is a permanent and an independent body established by the Constitution of India directly to ensure free and fair elections in the country. |
|
Article 324 |
It provides the power of superintendence, direction and control of elections to parliament, State legislatures, the office of President of India and the office of Vice-President of India shall be vested in the Election Commission. |
|
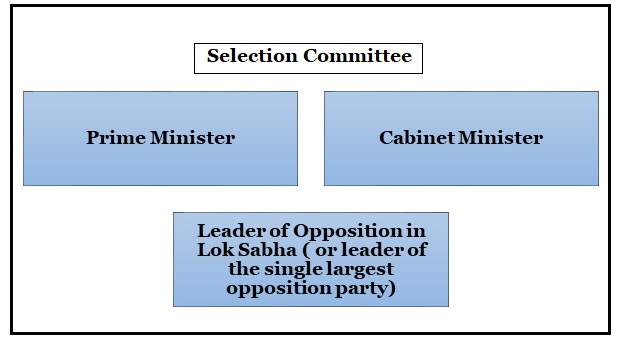
Composition |
It consists of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and two other Election Commissioners (ECs) |
|
Appointment |
The CEC and EC appointment is subject to the provisions of any law made by Parliament, be made by the President. |
Article 142 grants special powers to the Supreme Court to provide complete justice in any cause or matter pending before it.
References