900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
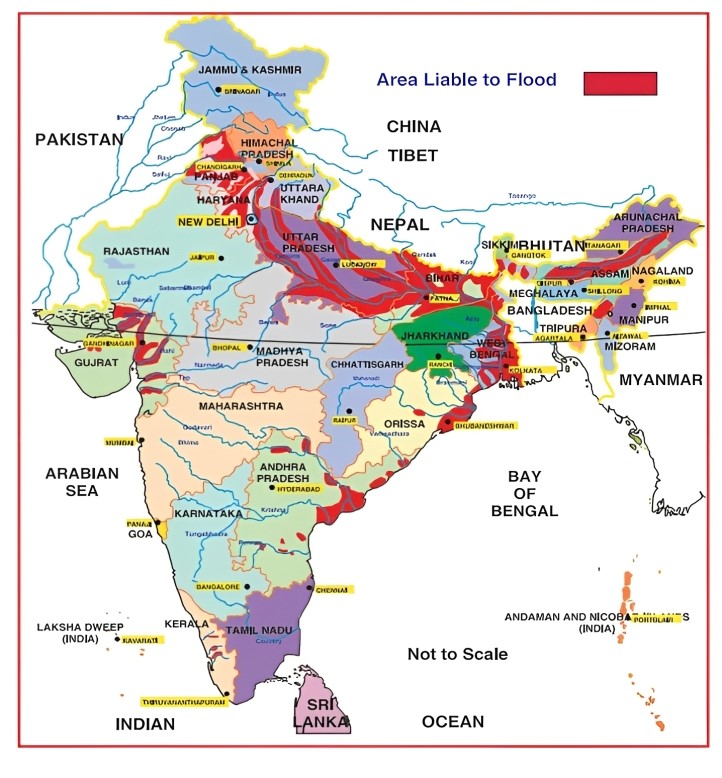
Recently, North India including Delhi witnessed heavy rainfall resulting in flood.
Urban flooding refers to the inundation of property in a built environment, particularly in more densely populated areas, caused by rain falling on increased amounts of impervious surfaces and overwhelming the capacity of drainage systems.
Meteorological Factors
Physical Factors
Human Factors
To Know about Part-II - Click Here.