900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
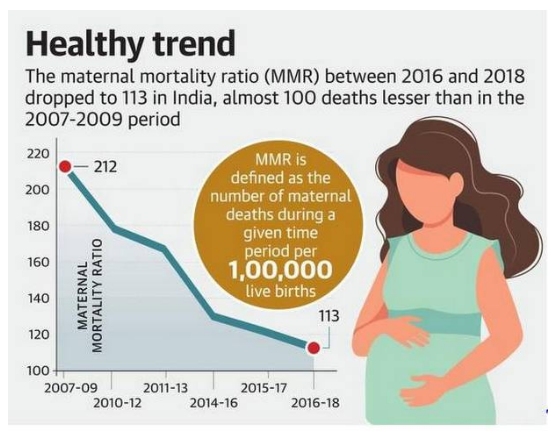
Sample Registration System
Bio-Markers
Ovarian Cancer
Farzad-B Gas Field
Anti Defection Law
Even without resigning, a legislator can be disqualified if by his conduct the Speaker/Chairman of the concerned House draws a reasonable inference that the member has voluntarily given up the membership of his party.
Kihoto Hollohan Judgment
US-India Business Council (USIBC)
Postal Ballot System
Source: The Hindu, Economic Times, Business Standard