900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
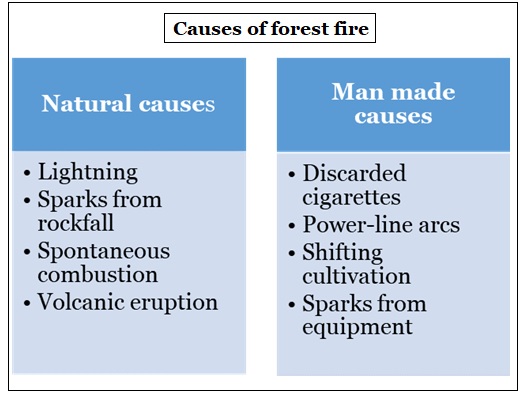
Forest fires have been raging in the Coonoor forest range in the Nilgiris in Tamil Nadu for almost a week.
|
Status of forest fire in India |
|
EHF is an index used to quantify heatwave intensity relative to the local climate, it provides an estimate of excess temperature based on the last 30 days’ excess and the last three days’ extreme temperatures
|
Steps taken by India to combat forest fire |
|