900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has proposed a Disclosure framework on Climate-related Financial Risks, 2024 to address the financial risks associated with climate change.
|
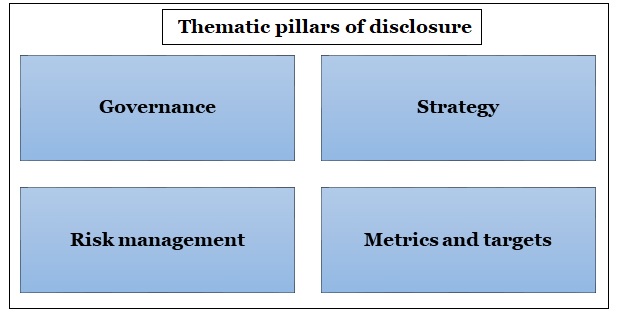
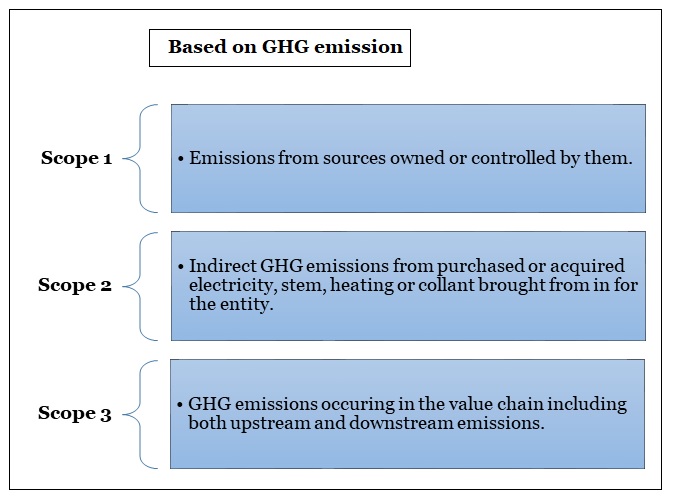
Risk categorization |
|
|
Physical risks |
Transitional risks |
|
|
References