SEBI has directed mutual fund houses to stop accepting any more inflows in schemes that invest in overseas exchange-traded funds (ETFs), starting April 1, 2024.
|
Key aspect |
ETFs |
Mutual Fund |
|
About |
They are passively managed funds that merely replicate an index, these funds usually hold all the stocks in the same weight as they are held by the underlying index. |
It is described as professionally managed investment schemes that collect money from various investors and then invest it in diversified holdings. |
|
Trading and liquidity |
They are traded on the stock exchange like any other stock, making them more liquid. |
They can only be bought or sold at the end of the day at the Net Asset Value price( It indicates one unit of mutual fund) |
|
Flexibility |
It is freely traded in the market and can be bought and sold as per the investor’s convenience. |
It can be bought or sold only by placing a request with the fund house. |
|
Cost structure |
They have lower expense ratios as they merely replicate the performance of the index. |
They have higher management fees as they are managed actively by an experienced fund manager. |
|
Commissions |
They are traded like any other share on the exchange, hence investors need to pay commission on scale and purchase units as per prevailing rules. |
There is no need to pay any commission for the sale and purchase. |
|
Investment approach |
They are passively managed, which means the fund mirrors a particular index, making them less risky and transparent. |
They are actively managed, which means fund managers invest in securities based on their analysis and market outlook. |
|
Minimum investment |
ETFs allow investors to start with smaller amounts. |
Mutual funds typically require a higher minimum investment. |
|
Taxation |
They are more tax-efficient as they have a lower capital gains tax. |
Mutual Funds are less tax-efficient. |
|
Diversification |
ETFs offer more targeted investments that mirror a particular index. |
Mutual funds offer more diversification options and exposure to a broader range of securities. |
|
Types |
There are mainly 5 types: equity ETF, bonds ETF, commodity ETF, international ETF and sectoral/thematic ETF. |
Equity schemes, Debt schemes, hybrid schemes, solution oriented schemes etc.,
|
Reference
Indian Express- SEBI halts overseas ETF
Delhi Chief Minister Aravind Kejriwal was recently arrested by the Enforcement Directorate (ED) in an excise policy case linked money laundering case
References
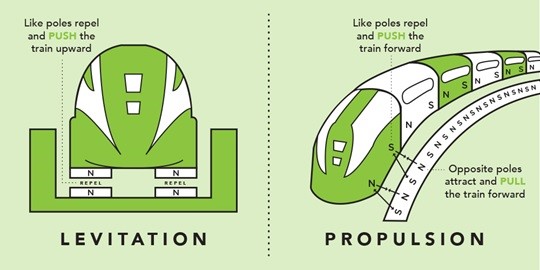
A Switzerland-based hyperloop company Swisspod Technologies signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with TuTr Hyperloop, a spin-off of IIT Madras to develop hyperloop systems in India.
|
Hyperloop in India |
|
Reference
Indian Express- Selling point for hyperloop
Millions of people living with chronic hepatitis B are unaware they have the virus.
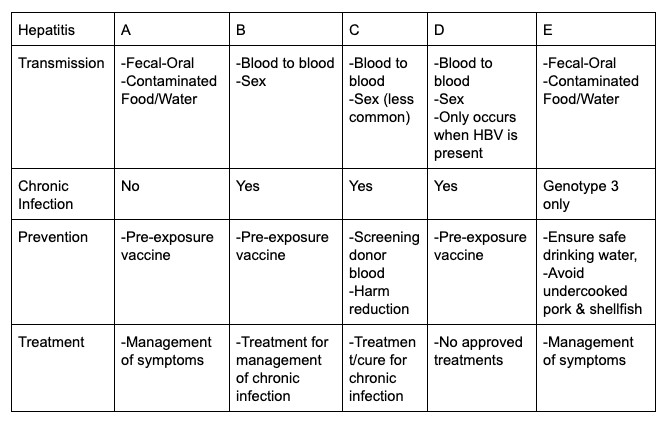
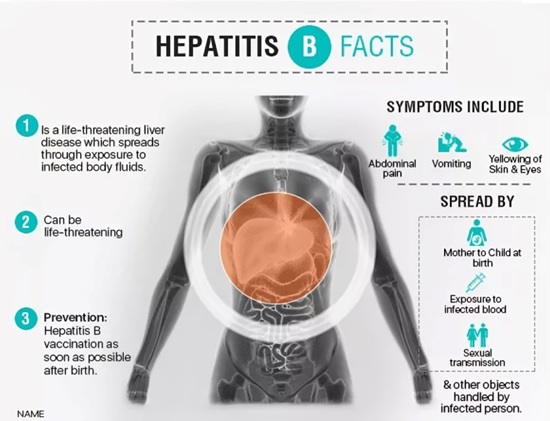
Hepatitis D, also known as “delta hepatitis,” only occurs in people who are also infected with the hepatitis B virus.
References
The Islamic State Khorasan (ISIS-K) has claimed responsibility for the attack at Moscow’s Crocus City Hall which resulted in at least 143 deaths and hundreds injured.
Major high profile attacks
|
Major terror outfits of the world |
Operation base |
|
Al-Qaeda |
It shifted based from Pakistan, Taliban -ruled Afghanistan and later expanded to other parts of the world, primarily in the Middle East and South Asia. |
|
Boko Haram |
It is active in Nigeria, Chad, Niger, Cameroon, and Mali. |
|
Harkat-ul-Mujahideen |
Pakistan and Afghanistan. |
|
Lashkar-e-Taiba |
It is a Pakistan-based group that primarily fights Indian control over Jammu and Kashmir. |
|
Jaish-e-Mohammed |
It is a Pakistan-based terrorist group active in Kashmir. |
|
Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL) |
It operates mainly in western Iraq and eastern Syria. |
References