900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
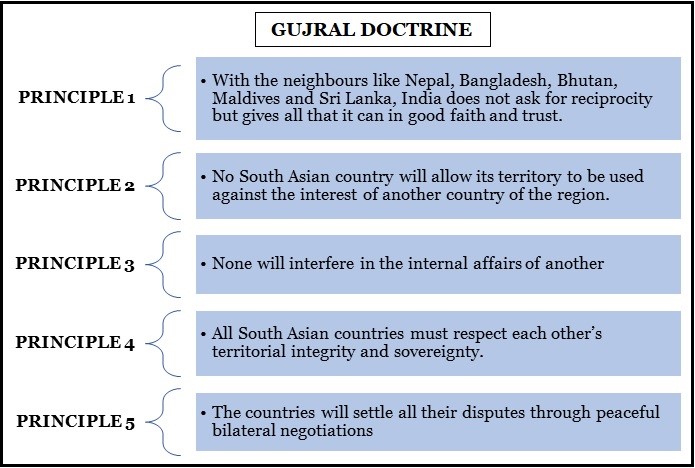
November 30 marks the 11th death anniversary of IK Gujral, the mastermind behind the doctrine that shaped India’s foreign policy.
Journalist Bhabani Sen Gupta coined the term “Gujral doctrine”.
Gujral named the countries from which India would not expect reciprocity, and it did not include Pakistan.
Mahakali Treaty has been signed in 1996 for the purpose of Integrated Development of the Mahakali River (known as River Sarda in India), including Sarda Barrage, Tanakpur Barrage and Pancheshwar Project.
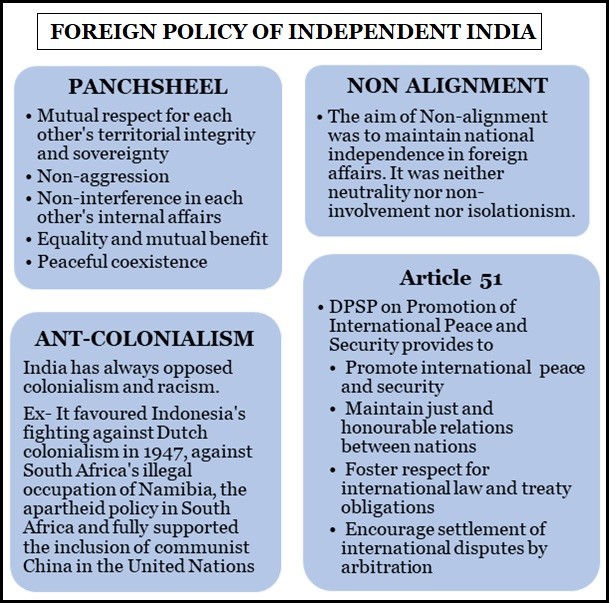
CTBT is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments.
References