900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The celebrations of this year’s Independence Day come amidst the talk of Indian economy reaching the 3rd largest spot by 2027.

To know more about India- the fastest growing economy click here
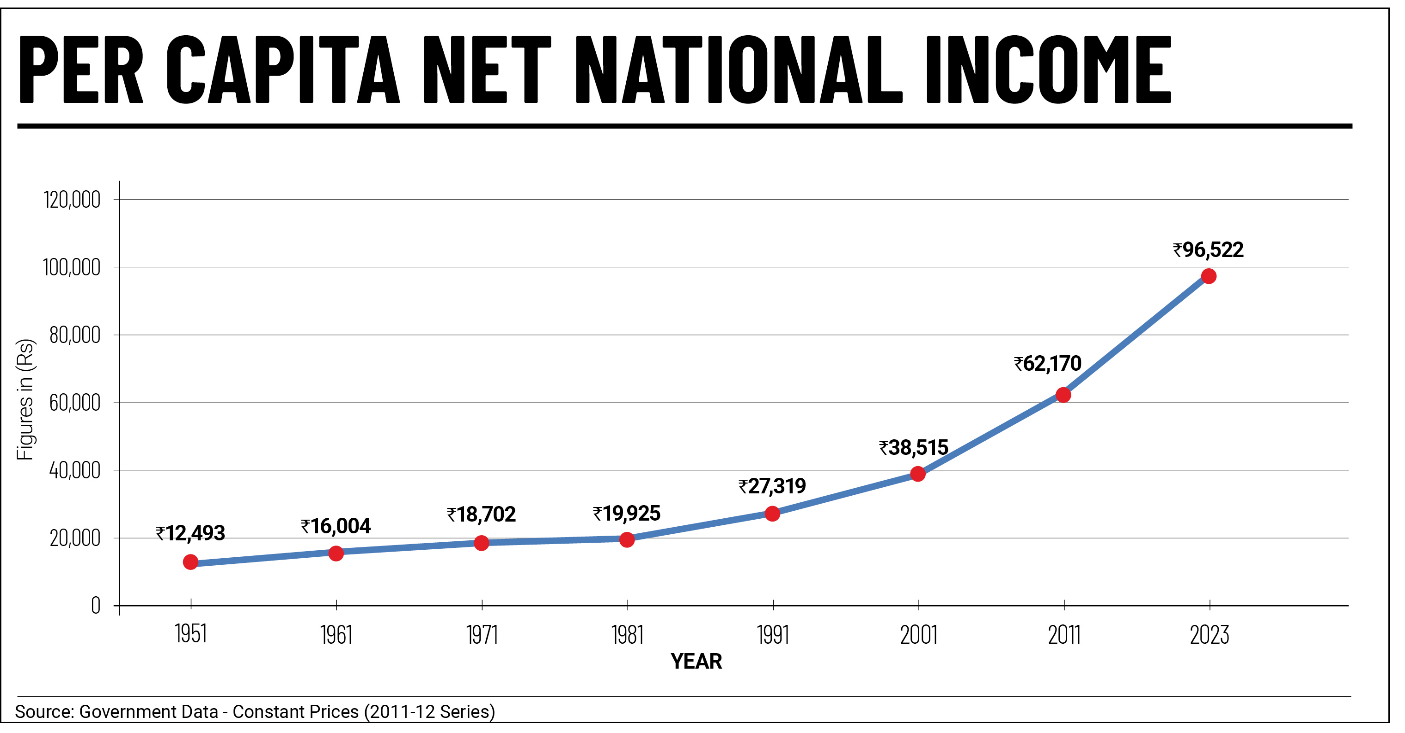
Social infrastructure is a term that refers to facilities that support social services Example- Health care, education etc.,
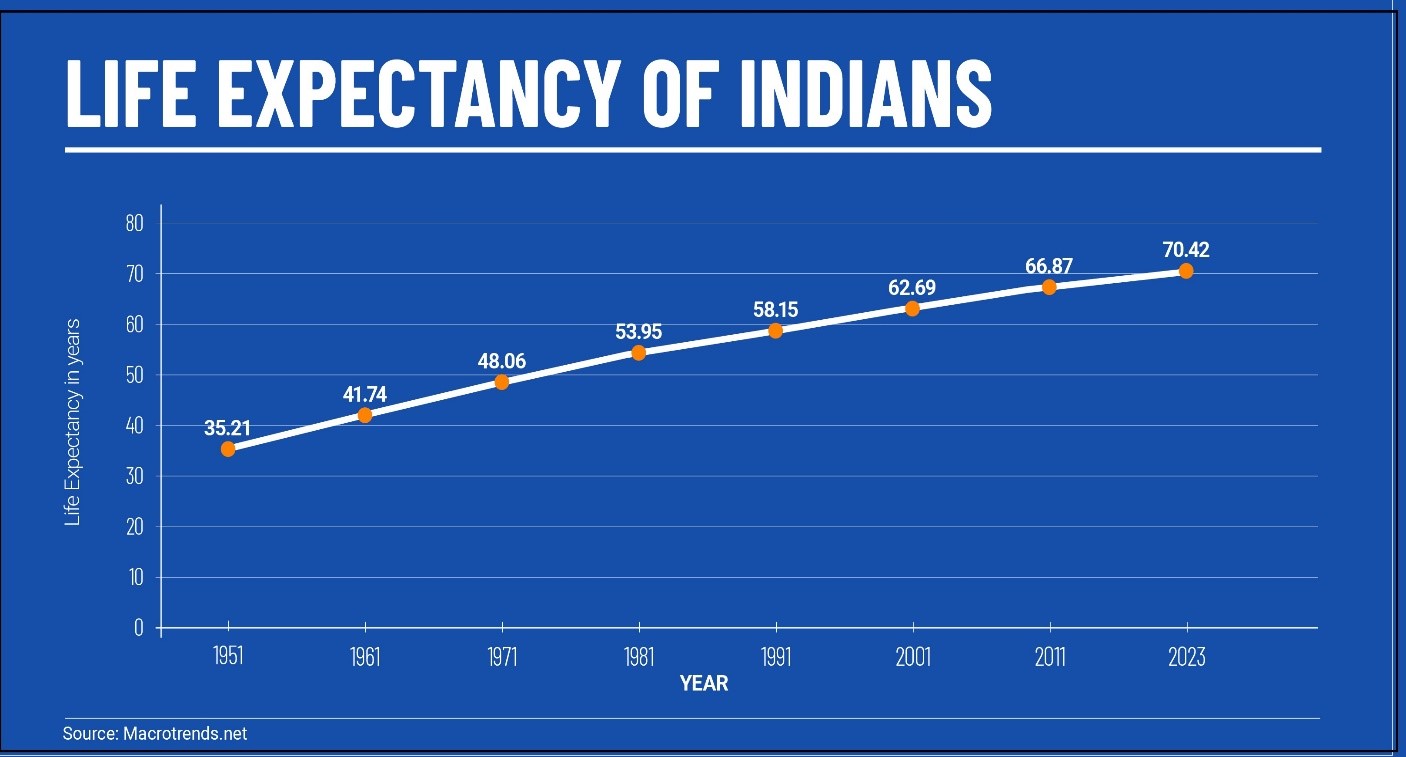
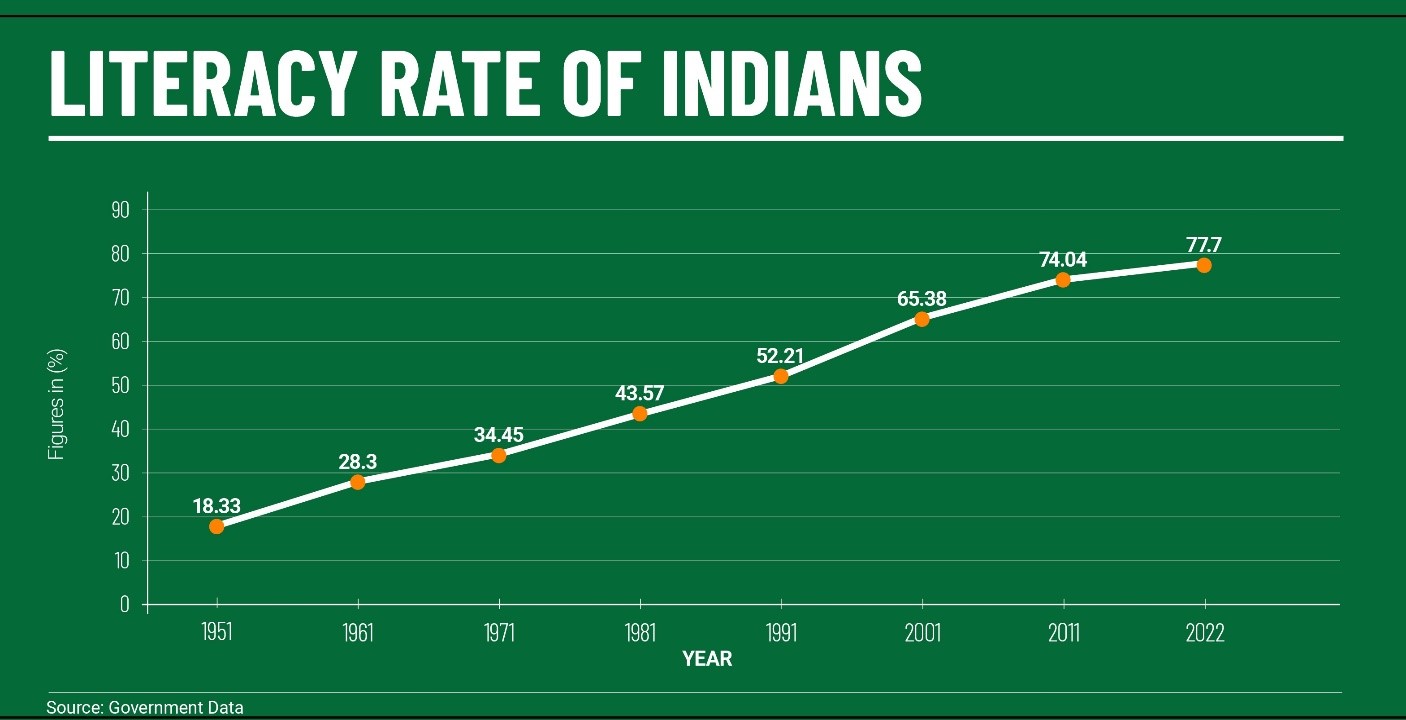
|
Key Decisions which shaped Indian Economy |
|
References