900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The announcement at the G20 Leaders’ Summit on the landmark India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to make India an Asian hub in global supply chains.
To know about the key outcomes of the G20 Summit, click here
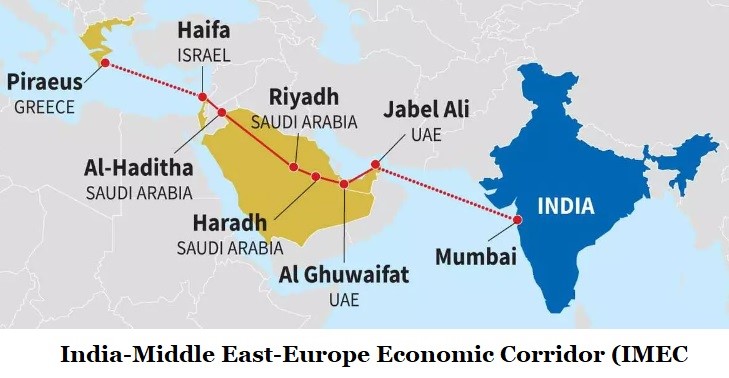
Supply chains refer to the geographical location of stages of production (such as design, production, assembly, marketing, and service activities) in a cost-effective manner.
Status of global supply chains
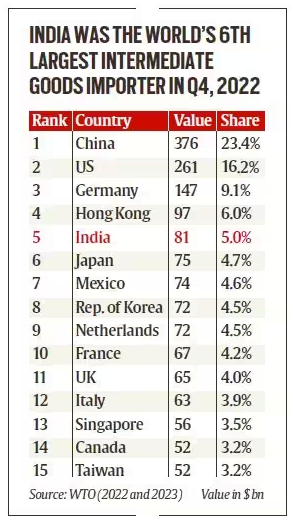
India, Japan and Australia has launched the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) in 2021 to attain strong, sustainable, balanced and inclusive growth in the Indo-pacific region.
References