900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
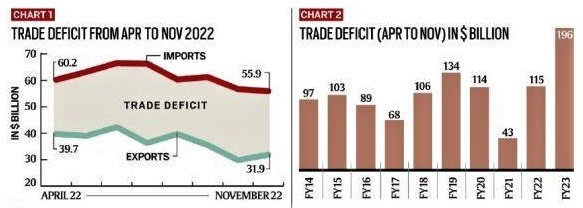
The latest trade data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry show a small increase in exports growth (32 billion dollars) and a fall in imports growth (56 billion dollars) in November 2022.
China is India’s second biggest trading partner after the United States.
References