900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
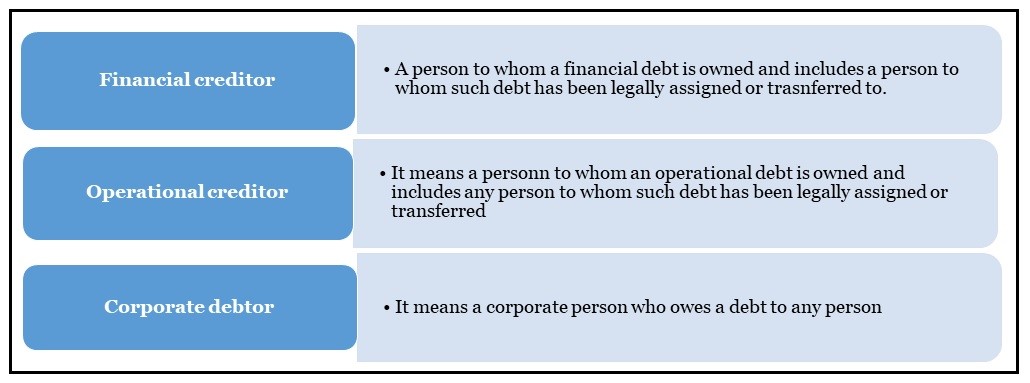
Financial creditors which had high expectations that the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 would help resolve the non-performing asset (NPA) problem, are deeply concerned over inordinate delays.
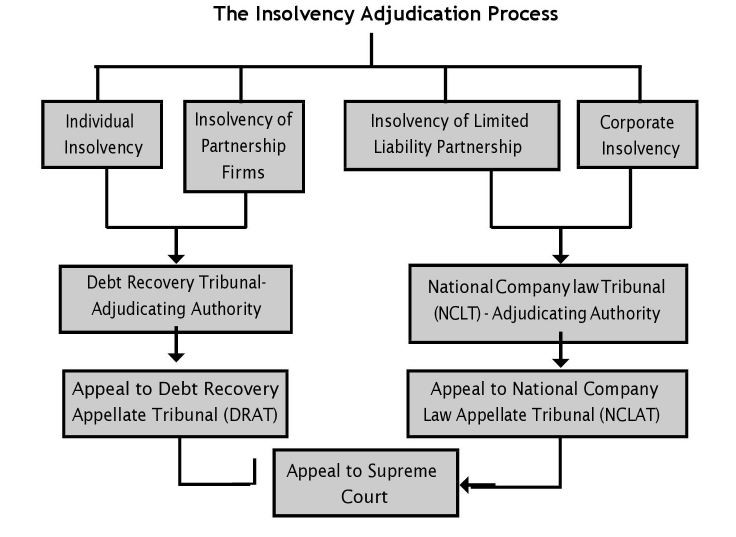
Insolvency is a situation where individuals or companies are unable to repay their outstanding debt.
|
Insolvency resolution |
Applicability |
Timeline |
|
Corporate insolvency resolution |
Companies (Can be applied in the event of default of at least 1 lakh rupees) |
330 days |
|
Personal insolvency resolution |
Individuals and partnership firms |
180 days |
Liquidation means closing down the business of the corporate debtor
To know more about Insolvency Bankruptcy Code 2016 click here
References