900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
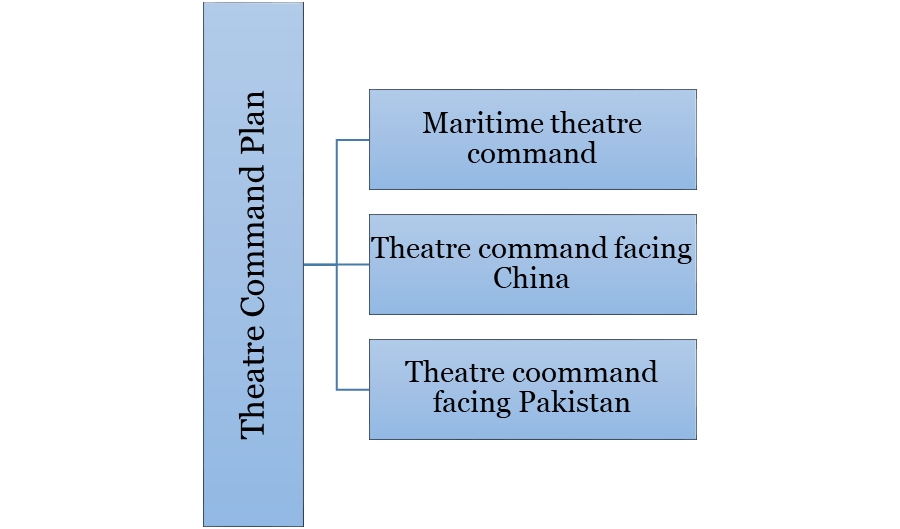
The passage of the Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill, by the Parliament is a step closer towards realising the long-awaited reform of theaterisation of the Armed Forces in India.
Issues
Establishment of theatre commands is a major military reform that seeks to roll the existing individual commands of the three services into tri-services organisations with a common military aim.
References