900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
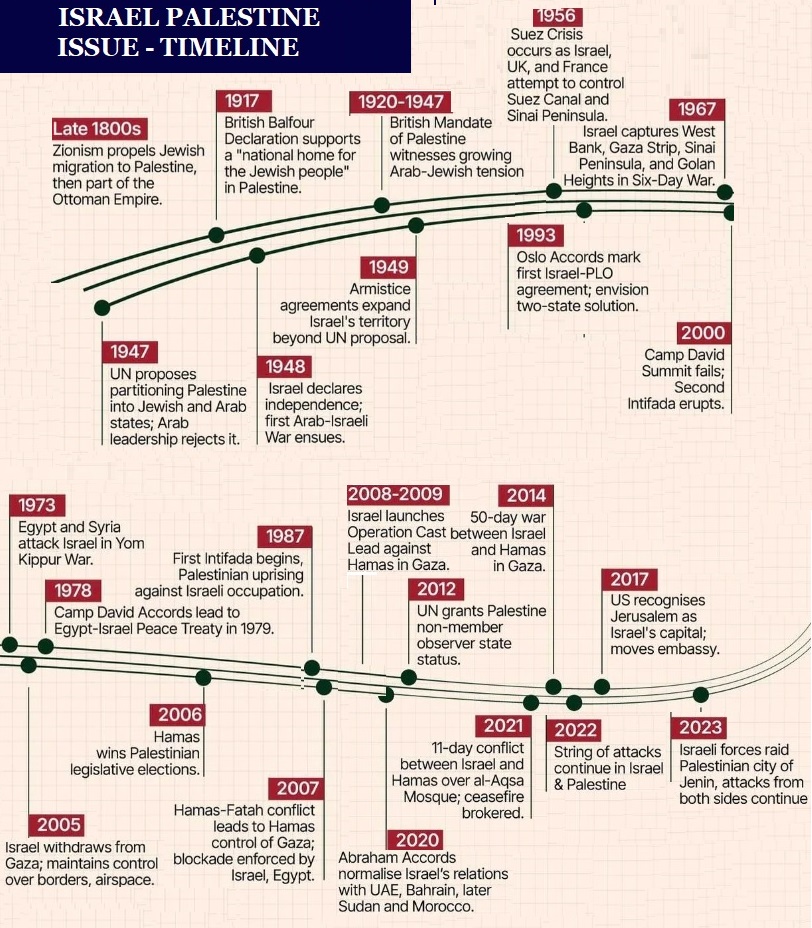
Recently Hamas, a Palestinian militant group launched a surprise attack on Israel which has led to the outbreak of war between Israel and Palestine.
|
Disputed Territories |
|
|
City of Jerusalem |
|

Egypt became the 1st Arab country to conclude a peace treaty with Israel.
|
ATTACKS ON GAZA |
|
|
Operation Cast Lead (2008) |
|
|
Operation Pillar of Defense (2012) |
|
|
Operation Protective Edge (2014) |
|
India was one of the last non-Muslim states to recognise Israel, and the first non-Arab state to recognise the PLO.
Operation Ajay was launched by the Indian government to repatriate Indians from Israel and Palestine through special chartered flights.
|
Mahatma Gandhi’s stand on Jewish nation state in Palestine |
|
References