900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
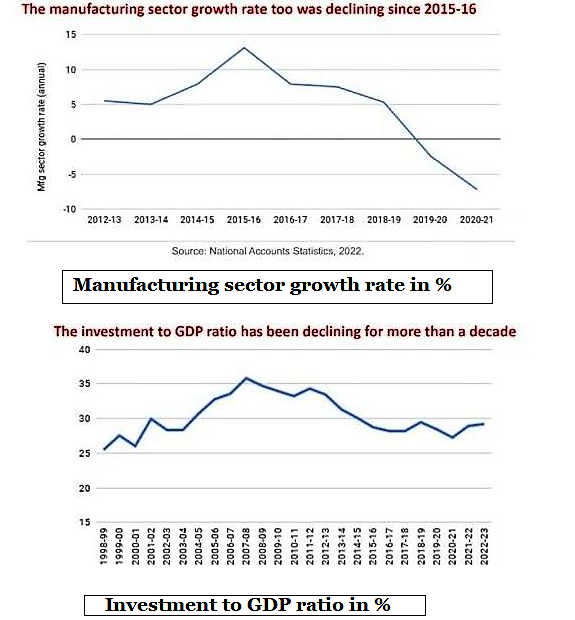
The growth rate of manufacturing productivity in India is in negative trend which got accelerated during COVID-19.
India is the 3rd most sought-after manufacturing destination in the world and has the potential to export goods worth US$ 1 trillion by 2030.
|
Steps Taken to Promote the Manufacturing Sector |
|
References