900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Higher education institutes in India can be the catalysts in integrating micro-credentials with existing academic programmes.
Microcredentials are short-duration learning activities with proof of specific learning outcomes that are validated through a standard and reliable assessment process.
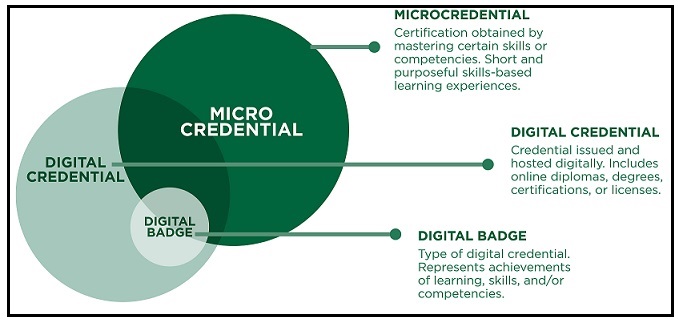
In macro-credential programmes, credit is based on the time spent in learning activities, such as lectures, labs, etc.,
The National Education Policy 2020 emphasizes the importance of providing skill-based education from school to higher levels.
|
National Credit Framework |
|
Reference
The Hindu- Micro-credentials the next step in higher education