900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Himachal Pradesh Chief Minister has requested Prime Minister to declare the destruction caused by heavy rains in the State as a national disaster.
|
Himachal Pradesh Rain |
|
|
Causes |
Impacts |
|
|
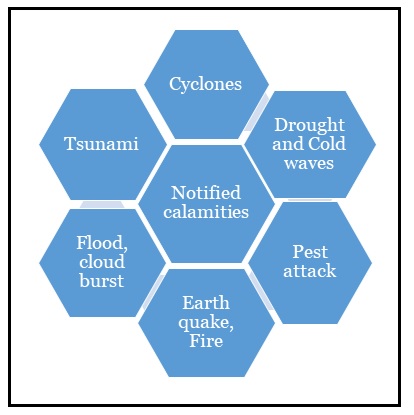
As of now, there is no executive or legal provision to declare a national calamity.
|
Institutional Mechanism |
Authority |
Head |
|
|
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) |
Prime Minister |
|
State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) |
Respective Chief Ministers |
|
|
District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) |
Either District Magistrate or District Collector |
References