The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) recommended the environmental release of the transgenic hybrid mustard DMH-11 for seed production and conduct of field demonstration studies.
GM Crops in India
|
Benefits of GM crops |
Drawbacks of GM crops |
|
|
Regulatory framework in India for GM crops
References
Dolphins have started coming back to the Ganga River with improvement in the quality of its water through the Namami Gange programme.
Bihar accounts for 50% of the world’s river dolphin population.
References
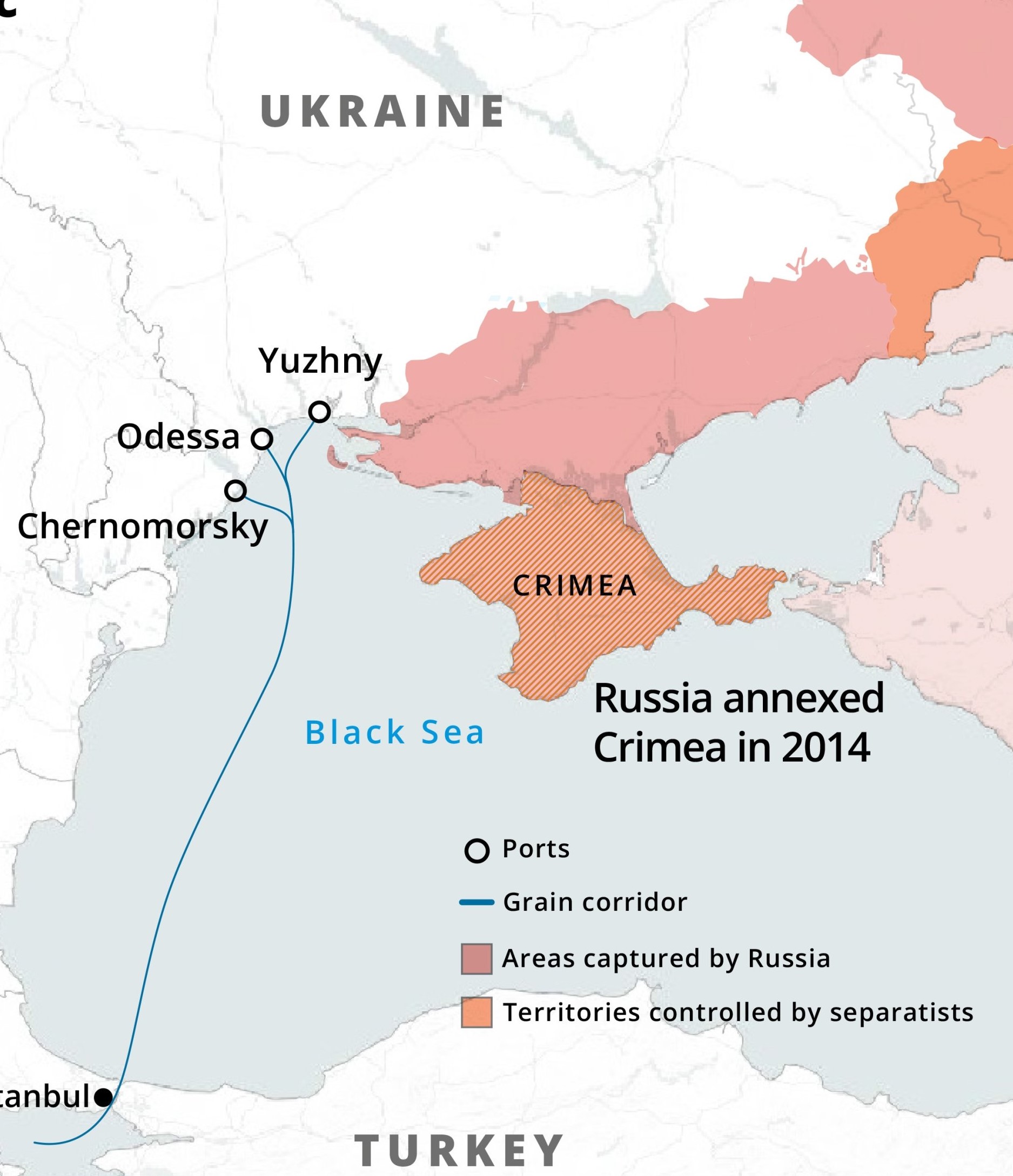
Russia suspended its participation to the Black Sea grain initiative a deal to allow food exports from Ukraine agreed amidst Russia-Ukraine war.
Ukraine is one of the largest grain exporters in the world. The initiative led to the export of more than 9 million tonnes of grains and other food products out of Ukraine.
Execution
References
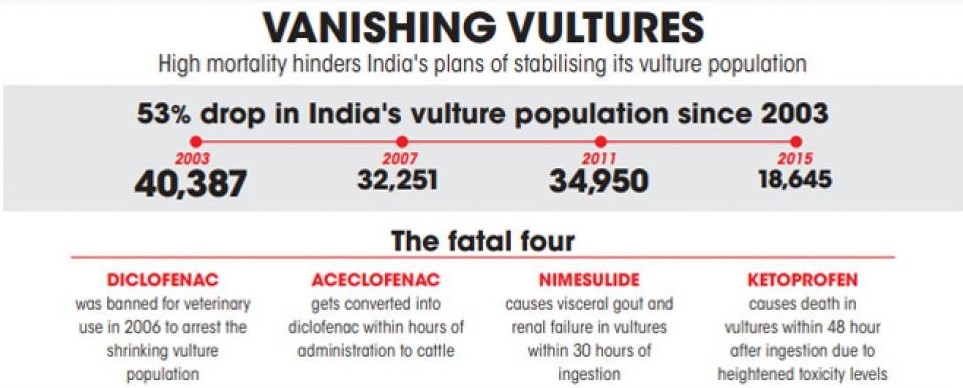
Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) has demanded a ban on using aceclofenac in cattle after a new study showed that the drug metabolises into diclofenac in water buffaloes.
Diclofenac, an anti-inflammatory drug, was banned for veterinary use by the Government of India in 2006.
Aceclofenac in water buffaloes poses the same threat to vultures as diclofenac in cattle.
References
New Zealand joins Rwanda, Cuba, Nicaragua, Mexico and the United Arab Emirates where at least half the lawmakers are women.
According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union, an international organisation of national parliaments, only 26% of lawmakers globally are women.
Rajkumari Amrit Kaur
Tarkeshwari Sinha
Vijaya Lakshmi Pandit
Sushila Nayyar
Indira Gandhi
Annie Mascarene
Geeta Mukerjee
References