Italy was planning to leave China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
Italy is the only G7 country to sign up for the BRI.
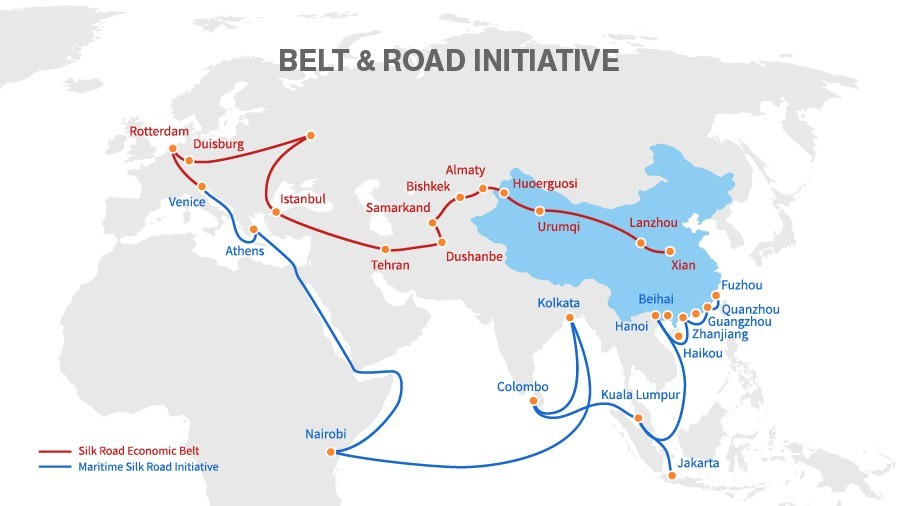
Related links- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
References
An earthquake of magnitude 6.8 struck Morocco claiming the death toll at over 600.
|
Oblique-reverse faulting
|
Morocco
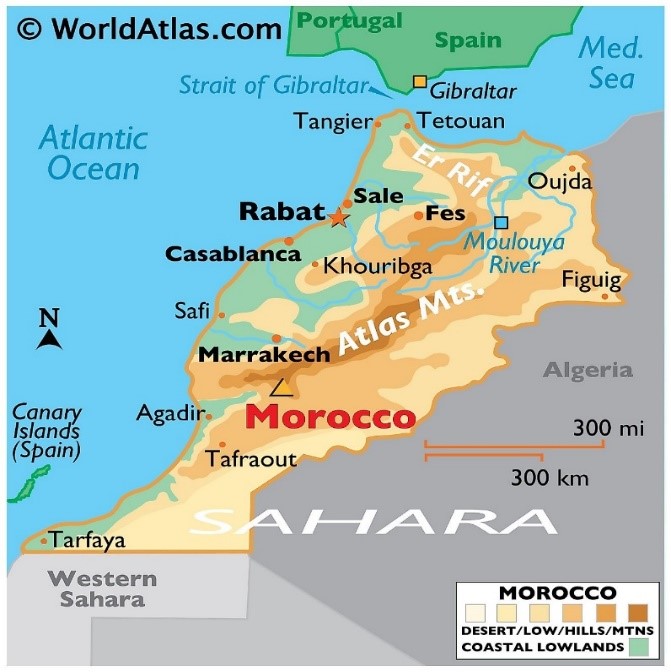
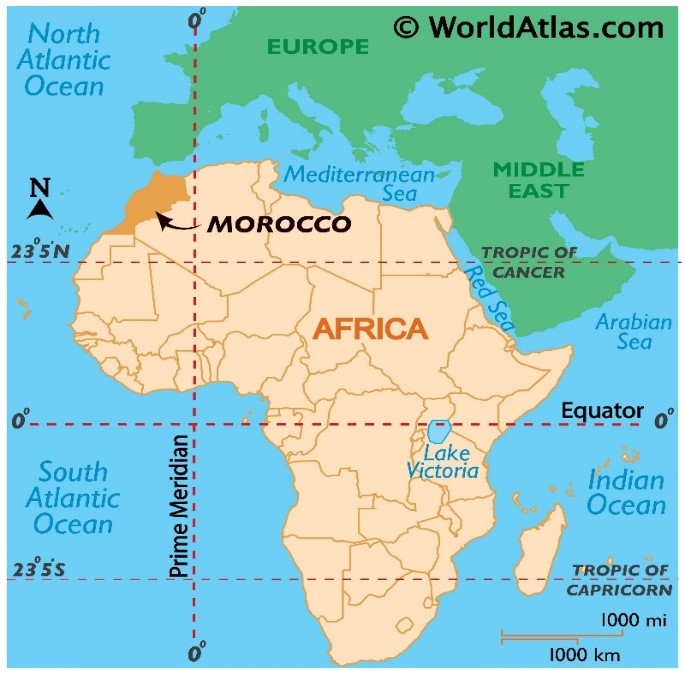
References
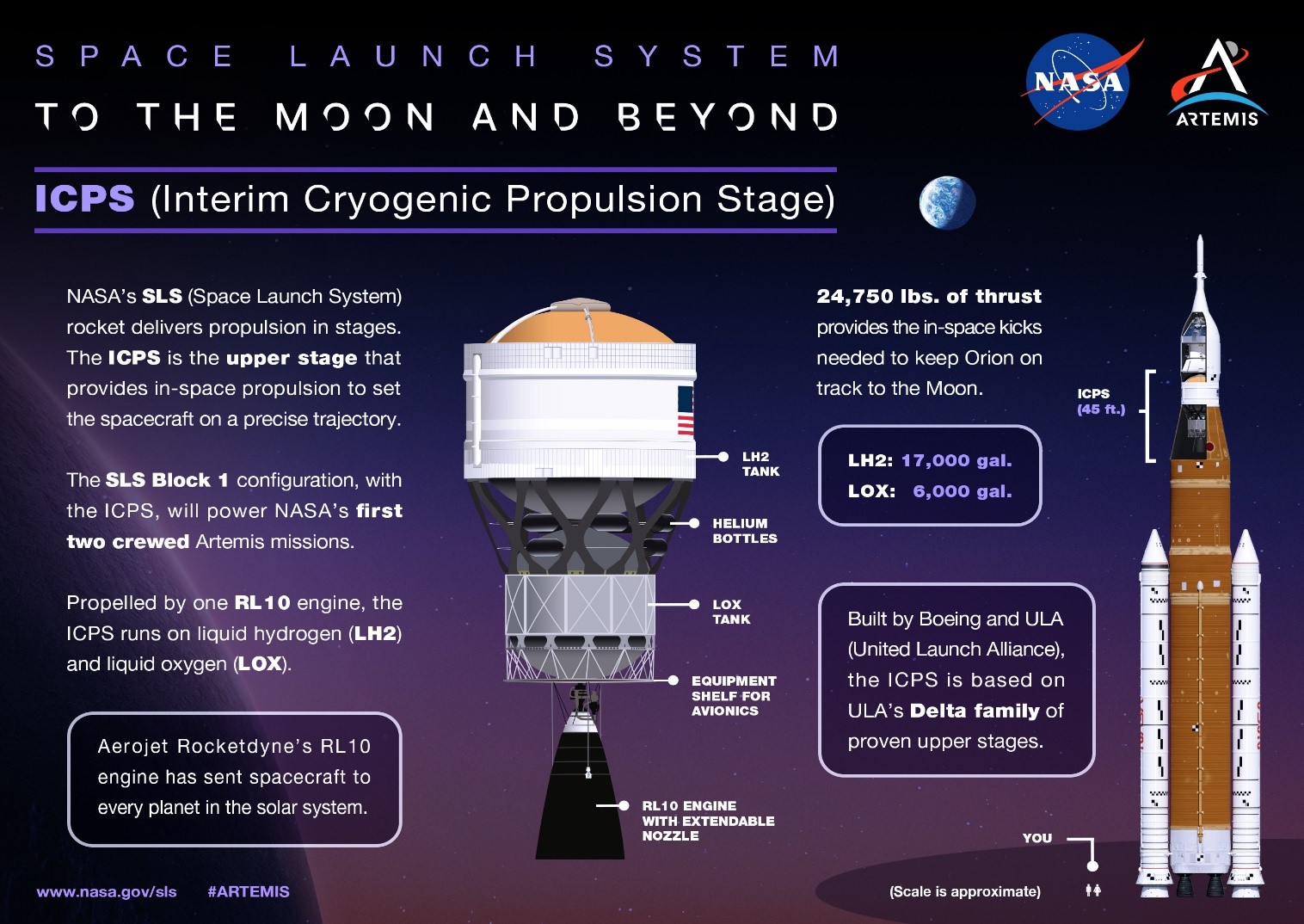
NASA and Elon Musk's SpaceX suffered setbacks in SLS (Unaffordable) and Starship (Explosive) programs recently.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Starship
References
The Backdrop of Nalanda Mahavira welcomes delegates at the G20 Summit for the President’s dinner.
References
The Ministry of Education is pushing States to open Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs) under the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR) recently.
The 1st VSK was inaugurated in June 2021 in Gujarat’s Gandhinagar.
Reference