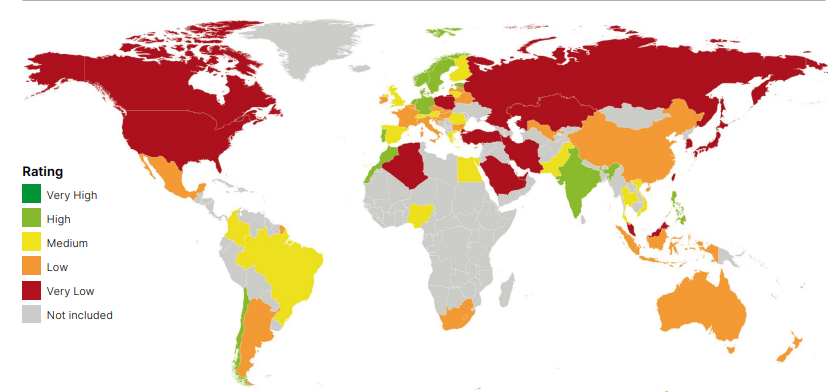
Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI)
CCPI 2024 was released at the COP 28 event in United Arab Emirates.
- It is an annual report, 1st presented at the COP 11 in 2005.
- Compiled by – 3 environmental NGO’s
- German watch, New Climate Institute and the Climate Action Network.
- Aim – To enable transparency in international climate politics and comparability of countries’ efforts and progress.
- Coverage – It covers major emitters, 63 countries and the EU, which together account for over 90% of global GHG emissions.
- Nigeria, Pakistan, UAE and Uzbekistan were added in CCPI 2024.
- Assessment - It uses 14 indicators under 4 categories
- GHG Emissions (40% weightage),
- Renewable Energy (20% weightage
- Energy Use (20% weightage)
- Climate Policy (20% weightage)
Climate Policy section evaluates countries policy working towards in achieving the Paris Agreement goals. CCPI uses per capita GHG emissions in its analysis.
CCPI 2024
- No one has occupied the 1st 3 ranks in the ‘very high’ performance category.
- Denmark retained the 4th with a score of 75.59% followed by Estonia and the Philippines taking 5th and 6th position respectively.
- India – It ranked 7th (8th in CCPI 2023), high ranking in the GHG emissions and Energy Use categories, but a medium in Climate Policy and Renewable Energy, as in the previous year.
While India is the world’s most populous country, it has relatively low per capita emissions as per CCPI 2024.
- G20 nations - 15 G20 countries receive an overall low or very low rating with Canada, Russia, the Republic of Korea, and Saudi Arabia being the G20’s worst-performing countries.
- EU – Overall, it rises 3 spots to 16th, where 14 EU countries are among the high and medium performers.
References
- Down To Earth| Climate Change Performance Index
- CCPI| Results of CCPI 2024
Cosmic Expansion
Euclid telescope observed that galaxies belonging to the Perseus Cluster and others move further away showing the expansion of universe.
Euclid telescope, designed and built by European Space Agency (ESA) to explore dark matter and dark energy which are thought to make up 95% of the universe.
- Cosmic expansion – The universe was born with the Big Bang as an unimaginably hot, dense point and at 10-34 of a second of big bang, it had an incredible burst of expansion known as inflation which expanded faster than the speed of light.
- Expansion rate – After inflation, it continued at a slower rate as the matter in the universe pulled on itself via gravity.
- About 5 or 6 billion years after the Big Bang, dark energy began speeding up the expansion again that continues even today.
Measuring the rate of expansion
- It is calculated using 2 models such as Lambda-cold dark matter (ACDM) and Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND).
- Lambda-cold dark matter (ACDM) – It is based on observation of the light left over from the Big Bang called as cosmic microwave background (CMB).
- Hubble’s constant – A value to predict how fast an astronomical object (star or galaxy) is moving away from us.
- It is about 43 miles (70 km) per second per Megaparsec meaning, a galaxy gains about 50,000 miles per hour for every million light years it is away from us.
- Hubble tension – It refers to the discrepancies in the expansion rate when measured using nearby galaxies and supernovas (exploding stars).
- It is 10% larger than when we predict it based on the CMB.
- Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) – It suggests that Newton’s law of gravity breaks down when the gravitational pull is very weak and the structure (such as galaxy clusters) would grow faster.
- Bulk flow – It is the average velocity of matter in a given sphere, which varies with the radius of the sphere.
The universe’s expansion makes galaxies move away from each other. The further away they are from us, the more quickly they move.
References
The Hindu| Measuring Cosmic Expansion
Otolith Rings
A new study published in ‘Nature’, tried to predict the effects of climate change on the physiological performance and distribution of organisms by studying the Otoliths.
- Otolith – They are small, white bio-mineralized ear stones in the head.
- Small calcium carbonate crystals are accumulated every day as very thin layers over a tiny core, and this forms an otolith.
- They are found in all fishes other than sharks, rays and lampreys but their shape and morphology is unique to each fish species.
- It contributes to both hearing and vestibular function in fish.
- Significance – When the fish dies the otoliths are preserved, separated from the decomposed fish body, and buried in the sediments of the sea floor unaffected for thousands of years.
- It records the age and growth of a fish from the date of hatch to the time of death and also reveals about fish’s health.
- Oxygen isotopes – It indicate the temperature the fish experienced when it was alive.
- Carbon isotopes – It reveal how quickly food was converted into energy.
- Otoliths relevance in climate change - Animals’ energy needs shift with temperature and studying the otoliths can help us predict which animals are most at risk from rising temperatures.
- Atlantic bluefin tuna in warmer waters had lower metabolic rates, showing that their bodies were unable to keep up with the energy costs of living in temperatures over 28°C.
References
The Hindu| Relevance of Otoliths in Climate Change
75th Year of Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
Human Rights 75 is an initiative to mark the 75th anniversary of Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Human Rights 75, an initiative whose 3 main goals focus on universality, progress and engagement under the leadership of UN Human Rights, together with its partners.
- UDHR – A global document that establishes the human rights and civil liberty of every person in the world.
- It consists of a preamble and 30 articles setting out fundamental rights and freedoms.
- Basis – Vienna Declaration and Program of Action of 1993.
- Proclaimed by – The United Nations General Assembly in Paris on 10 December 1948 (UNGA resolution 217 A).
UDHR sets out, for the 1st time, fundamental human rights to be universally protected and it has been translated into over 500 languages. Human Rights Day is celebrated annually around the world on 10 December every year to honour the UN Assembly adoption of UDHR.
- Legality – It isn’t a treaty and isn’t legally binding in itself, but it is viewed as the basis for international human rights law.
- Achievements – It have inspired and paved the way for more than 70 human rights treaties at global and regional levels.
- It inspired the decolonization movement, anti-apartheid movement and on gender issues and even on LGBTIQ+ issues.
- India is a signatory to this declaration.
References
- The Indian Express| 75th Year of UDHR
- UN.ORG| Universal Declaration of Human Rights
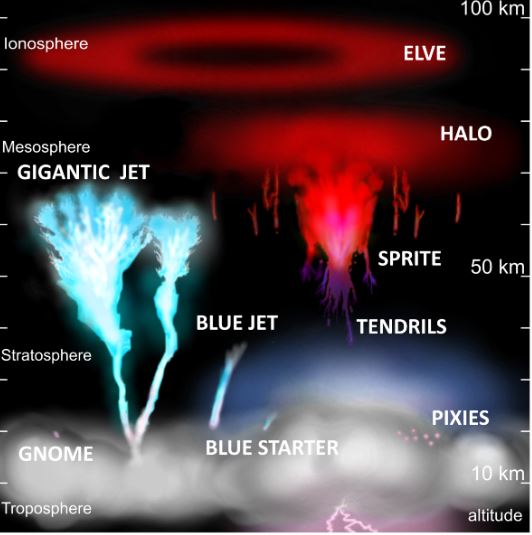
Red Sprite
The European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut captures images of red sprite from ISS Cupola observatory.
- It is dubbed as red lightening which lasts merely a millisecond.
- It is a part of transient luminous event (TLE), a rare electrical discharge that can appear over thunder clouds.
Unlike typical lightning bolts that descend from the clouds to the ground, a sprite behaves inversely, ascending into the atmosphere, resembling a form of reverse lightning.
- Location – It forms between 40 and 80 kilometers above Earth and is rarely visible from Earth.
- Thor-Davis ISS experiment – It aims to investigate upper atmospheric lightning and its implications on greenhouse gas levels, thereby influencing global warming.
- It will photograph storms from the vantage point of the International Space Station's (ISS) observatory.
- Davis Camera – It works like the retina in our eyes that is sensitive to changes in light, allowing it to take up to the equivalent of 100.000 pictures per second.
Reference
NDTV| Red Sprite
|
Other Important News
|
|
Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi)
- YUVAi is a national program that aims to teach AI skills to students in grades 8–12.
- The program is a collaboration between the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), and Intel.
|
|
Zhuque-2 rocket
- The Zhuque-2 (ZQ-2) is a Chinese medium-sized, 1st methane-fueled rocket to reach orbit.
- The rocket can carry a payload of up to 1.5 metric tons into a 500-kilometre-orbit.
- The rocket is powered by liquid oxygen and liquid methane.
- It was launched by China-based private space technology firm LandSpace.
|
|
“Operation Storm Makers II”
- Operation Storm Makers II was a global operation by Interpol that targeted human trafficking and migrant smuggling.
- The operation targeted criminal networks that exploit migrants for cyber fraud.
- The operation involved law enforcement agencies in 27 countries across Asia and other regions.
|
|
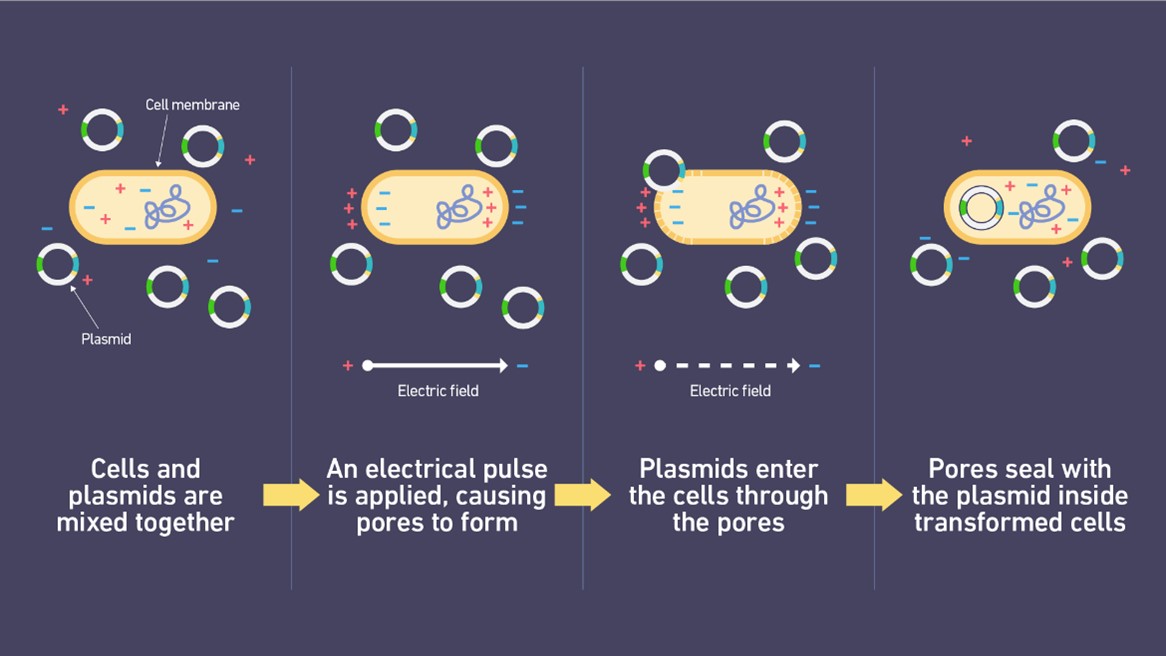
Electroporation
- A recent study found that electric eels can release enough electricity to genetically modify small fish larvae, which is known as electroporation, a gene delivery technique.
- Electroporation is a technique that uses an electrical field to increase the permeability of cell membranes.
- This allows larger molecules, such as DNA, drugs, and chemicals, to enter the cell.
|
|
Poshan Innovation Platform (PIP)
- Aim - To improve the nutritional status of mothers and children under five years of age, at the last mile.
- Launched by - India Nutrition Collaborative in partnership with the office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India.
- India ranked 111 of the 125 in the Global Hunger Index 2023.
|
|
Green turtle (Chelonia mydas)
- The green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas) is the largest hard-shelled sea turtle.
- Green sea turtles are found in temperate and tropical waters around the world. In India, they can be found on the west and east coasts, Andaman & Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.
- Green sea turtles are mainly herbivorous and eat sea grass.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN – Endangered
- Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act.
|
|
China's Belt & Road Initiative
- Italy withdraws from China's Belt and Road project recently.
- China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a connectivity project that aims to revive the ancient Silk Road.
- The BRI was announced by Chinese President Xi Jinping in 2013.
- It aims to connect China with Europe by land and rail, and to Asia and Africa by sea.
|
|
Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR)
- 4 soft release centres being set up in Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR) will be guarded by solar fencing recently.
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR) is located in Jharkhand, established in 1973 as part of Project Tiger.
- It is one of the first 9 tiger reserves created in the country at inception of 'Project Tiger'.
- It is the only tiger reserve in Jharkhand. It forms part of Betla National Park and Palamau Wildlife Sanctuary.
|
|
Eastern Ghats Nature Interpretation Centre
- A first-of-its-kind Eastern Ghats Nature Interpretation Centre in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh has been inaugurated recently.
- It is a project within the development of the Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary.
- A nature interpretation centre is a museum that aims to educate visitors about the importance of nature conservation.
|
|
Gangetic Dolphin
- Uttar Pradesh has made the Gangetic Dolphin as the state’s aquatic animal recently.
- The dolphin has already recognized as the national aquatic animal.
- These dolphins are found in rivers like Ganga, Yamuna, Chambal, Ghaghra, Rapti, and Gerua.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN - Endangered species.
- Schedule –I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Project Dolphin - Launched in 2016 by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG).
|
